Figure 7.
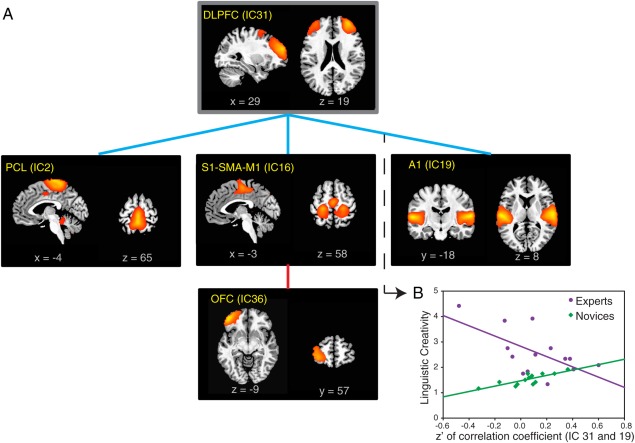
Distinct associations between linguistic creativity ratings and connectivity patterns in experts and novices.
(A) An analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) model was used to examine group differences in the way linguistic creativity scores were correlated with functional connections in experts and novices. In experts, linguistic creativity scores were more weakly correlated with the strength of functional connections between sensorimotor (somatosensory, premotor and auditory) areas and the DLPFC (indicated by blue lines, see an example in Fig. 7B) while these scores were more strongly correlated with the strength of functional connection between sensorimotor area and the left orbitofrontal cortex (indicated by the red line) (FDR < 0.05 in each instance). (B) The relationship between ICs 31 and 19 is used to illustrate an instance in which linguistic creativity scores and functional connections between ICs were more weakly correlated in experts than in novices. The correlation (slope of the linear fit) between LC and Fisher's z’ transformed correlation coefficient (of IC 31 and 19) is significantly less (P = 0.002, FDR = 0.04) in experts (purple: y = −2.02 × x + 2.82, P = 0.02) than in novices (green: y = 1.05 × x + 1.47, P = 0.0009). A1, primary auditory cortex; OFC, orbitofrontal cortex; PCL, paracentral lobule; SMA, supplementary motor area; S1, primary somatosensory cortex.
