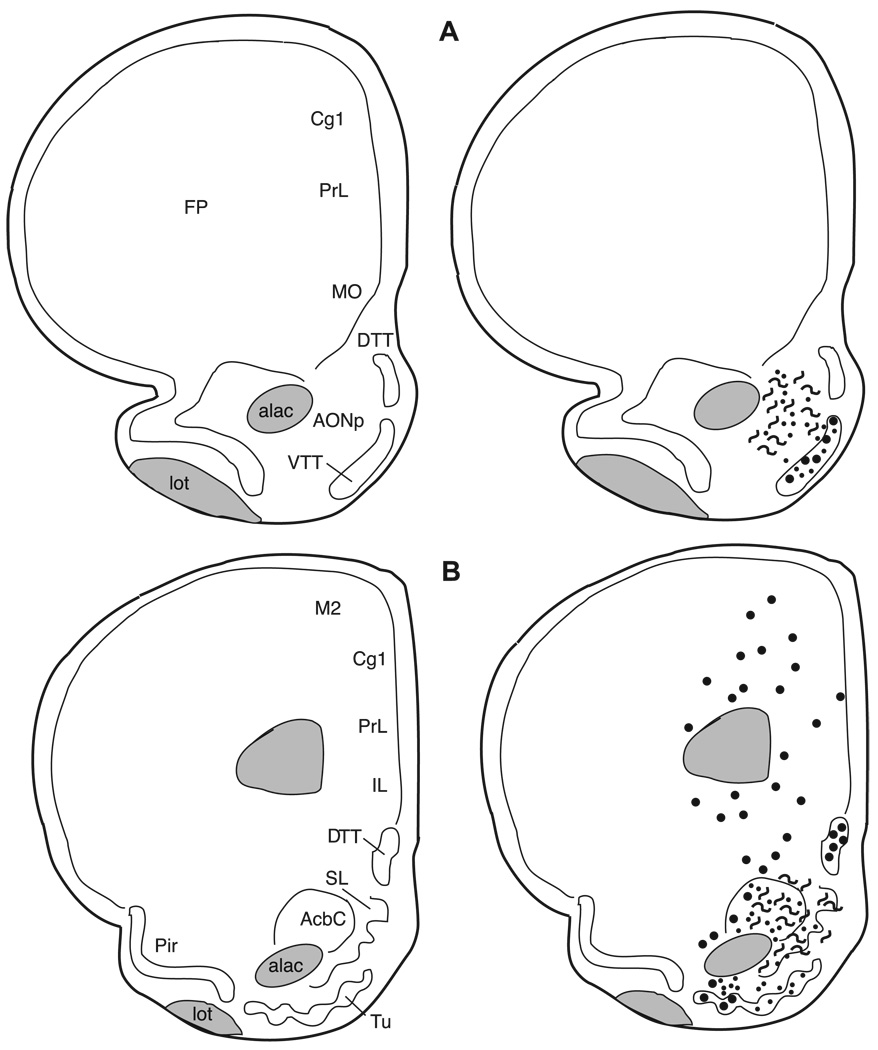
Fig. 7.
The distribution of enkephalin immunoreactive cells, fibers, and terminals throughout the forebrain and midbrain of the male Syrian hamster. The circles represent enkephalin immunoreactive cell bodies, the squiggly lines represent enkephalin immunoreactive fibers, and the dots represent enkephalin immunoreactive terminal fields. The mapping illustrated here represents a composite of the most consistently labeled regions from six colchicine-treated brains and two non-colchicine-treated brains.