Figure 5.
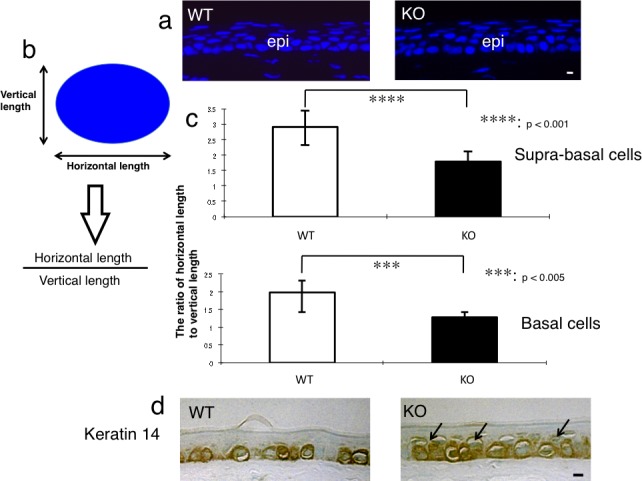
Evaluation of intraepithelial differentiation of the corneal epithelium. (a) In order to evaluate the morphology of the nuclei of the basal and suprabasal cells of the corneal epithelium, the tissue was stained with DAPI nuclear staining. Scale bar: 10 μm. (b) The ratio of horizontal/vertical length of the nucleus of suprabasal or basal cell was calculated to evaluate the intraepithelial differentiation of an epithelial cell. (c) The ratio of horizontal/vertical length of the nuclei of suprabasal cells and of basal cells was significantly lower in the corneal epithelium of the adult KO mice than in adult WT mice. ***P < 0.005 and ****P < 0.001 by unpaired Student's t-test. Bar: standard error. (d) Keratin 14, a marker of basal epithelial cells, was detected in the basal cells of the corneal epithelium of a WT mouse, while both basal and suprabasal cells (arrows) were labeled for keratin 14 in the corneal epithelium of a KO mouse. Scale bar: 10 μm.
