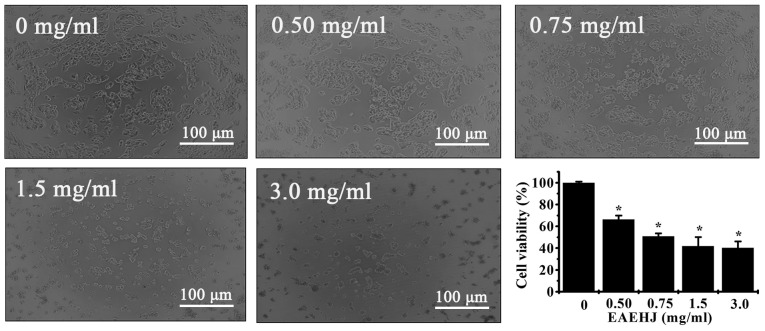
Figure 1.
Effects of Hypericum japonicum ethyl acetate extract (EAEHJ) on cellular morphological changes and cell viability of HepG2 human hepatoma cells. The HepG2 human hepatoma cells were treated with various concentrations of EAEHJ for 24 h, and cellular morphological changes were subsequently observed using phase-contrast microscopy. The images were captured at a ×100 magnification for each experiment performed in triplicate. Cell viability was assessed using an MTT assay. The MTT assay indicated that EAEHJ treatment significantly reduced HepG2 human hepatoma cell viability in a dose-dependent manner. The data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation from three independent experiments. *P<0.01, vs. the control cells (100%, treated with 0.5% dimethyl sulphoxide vehicle).