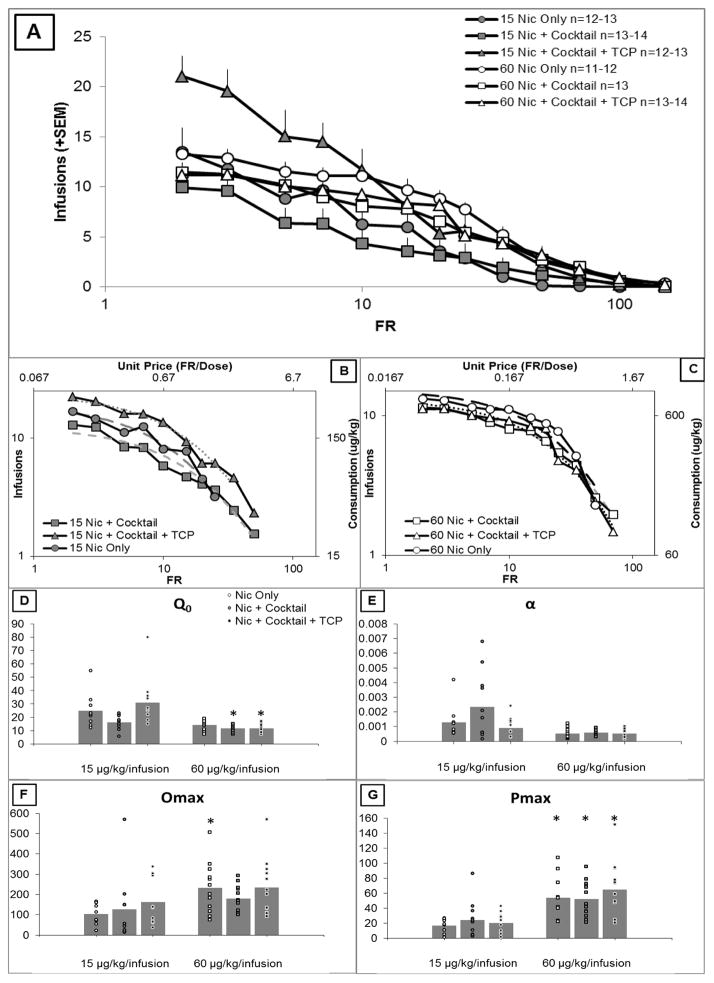
Figure 4.
A) Average number of earned infusions on the last two sessions of each FR for each group. B and C) Average demand curve for each group responding along with the best fit of Equation 1. C–F) Demand parameters for all six groups. Bars represent group averages and data points represent individual rats. A 3×2 ANOVA (nicotine dose X group) was conducted for each parameter. Follow-up 2 × 2 ANOVAs were conducted to further delineate the effect of group as described in section 2.4. Significant pairwise comparison to low nicotine dose is indicated by *, p < 0.05. C) Q0 is a free parameter representative of estimated consumption if the drug were free. There was a significant main effect of nicotine dose (p < 0.05), and a significant main effect of group (p < 0.05) that interacted with nicotine dose (p < 0.05). There was no effect of adding cocktail to the nicotine solution. However, adding TCP to the cocktail solution significantly increased demand intensity (p < 0.05), and this effect interacted with nicotine dose (p < 0.05). Adding cocktail along with TCP did not affect demand intensity. D) α is a free parameter estimating sensitivity to cost and might be thought of as inversely related to essential value of the reinforcer. There was a significance main effect of nicotine dose (p < 0.05), and there was a significant effect of group (p < 0.05), but no nicotine dose X group interaction. Adding cocktail to the nicotine solution had no effect on sensitivity to cost. Adding TCP to the cocktail solution decreased sensitivity to cost, and this effect significantly interacted with nicotine dose (p < 0.05). Adding cocktail along with TCP to the nicotine solution had no effect on sensitivity to cost. E) Omax is an estimate of maximum reinforcer consumption. There was a significant main effect of nicotine dose (p < 0.05), but no effect of group or nicotine dose X group interaction. F) Pmax is an estimate of the price that produces maximum consumption. There was a significant main effect of nicotine dose (p < 0.05), but no effect of group or nicotine dose X group interaction. Follow-up 2 × 2 ANOVAs did not reveal any significant effects between groups or interactions with dose.