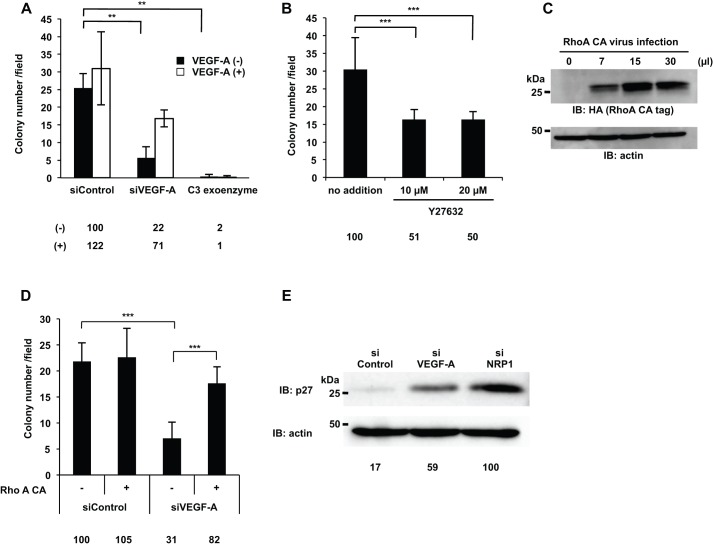
Fig. 6.
RhoA activity was essential for the DJM-1 cell proliferation signal to induce p27kip1 protein degradation. (A,B) The colony formation assay for DJM-1 cells. (A) DJM-1 cells were treated with siRNAs (siControl, siVEGF-A, 20 nM each) and C3 exoenzyme (2 μg/ml) in the presence or absence of exogenous VEGF-A (1 µg/ml), indicated as white columns (+) or black columns (−), respectively. (B) DJM-1 cells were treated with the ROCK inhibitor, Y27632 (10 or 20 μM). (C) An increase in the lentiviral infection of RhoA constitutively active form (RhoA CA) enhanced the RhoA active form in DJM-1 cells. (D) The colony formation assay for siRNAs (siControl or siVEGF-A, 20 nM each) treated-DJM-1 cells with (+) or without (−) RhoA CA expression. Percentages from each relative to the siControl (−)(A,D) or no addition (B) are shown below the graph. (E) DJM-1 cells were treated with siControl, siVEGF-A, or siNRP1 (20 nM each) under anchorage-independent conditions and total cell lysates were immunoblotted with an anti-p27 antibody. Percentages from the p27 level in each siRNA treated-cell lysate relative to siNRP1 are indicated below the lane. The same proteins were re-immunoblotted with an anti-actin antibody to normalize the amounts of each protein. These data represent the means±s.d. **P<0.005; ***P<0.001.