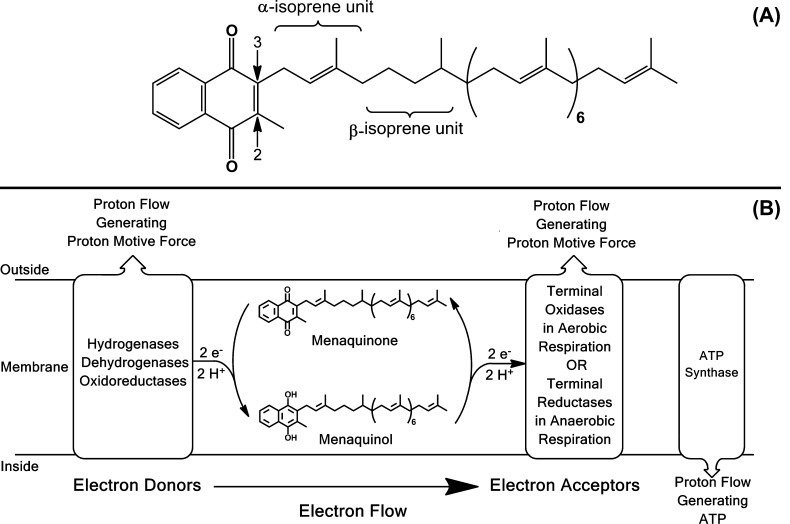
Figure 1.
Structure and role of mycobacterial menaquinone. (A) Mycobacterial menaquinone has 9 isoprene units with the one in the β-position hydrogenated as previously determined7 and is designated MK-9(II-H2) following the IUPAC-IUB recommendations for nomenclature of quinones with isoprenoid side chains (http://www.chem.qmul.ac.uk/iupac/misc/quinone.html). The arrows indicate carbons 2 and 3 of the naphthoquinone ring. (B) The role of menaquinone in mycobacterial respiration and oxidative phosphorylation. In respiration, menaquinone accepts electrons from a variety of electron donors and transfers them to terminal oxidases or reductases. Subsets of the electron donors and acceptors pump protons to the outside of the cell generating proton motive force that can be utilized to generate ATP via oxidative phosphorylation. The energetics of mycobacteria respiration and oxidative phosphorylation have been reviewed recently.56