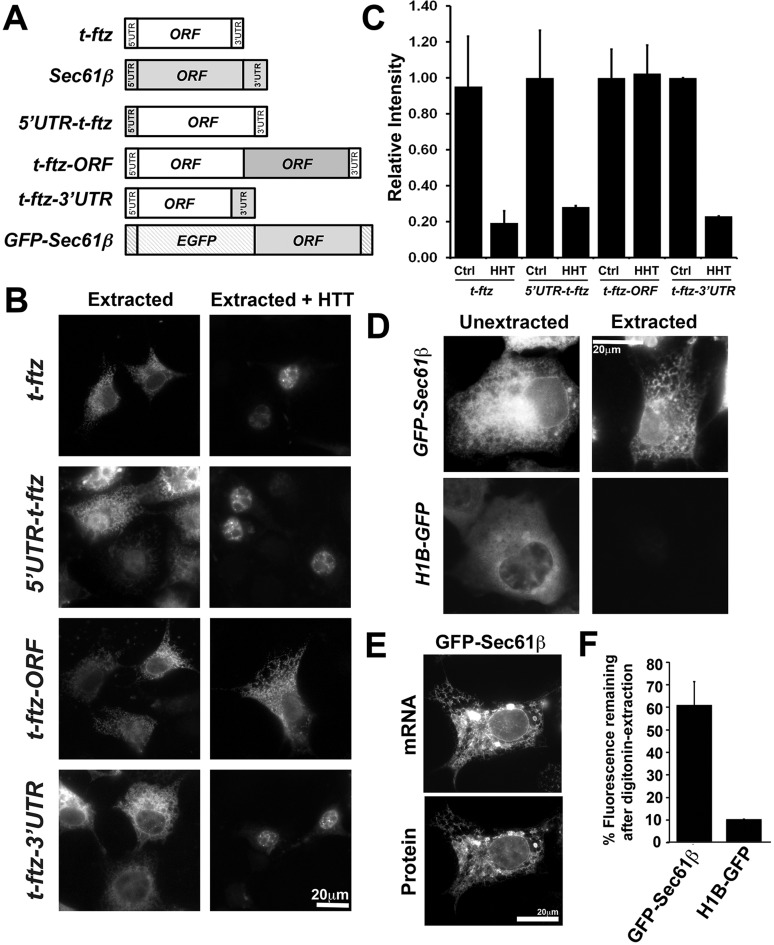
Fig. 2.
Overexpressed GFP-Sec61b mRNA is associated with the ER membrane. (A) Schematic diagram of constructs. All t-ftz sequences are shown in white, Sec61b sequences are shown in gray and EGFP sequences are shown as hatched boxes. (B,C) Chimera plasmids containing either the Sec61b 5′UTR, 3′UTR or the ORF fused to t-ftz were transfected into COS7 cells. At 18–24 h post-transfection, cells were treated with either control or HHT, followed by digitonin extraction to remove cytoplasmic contents. Cells were fixed, stained using FISH probes against ftz, and imaged. (D–F) Plasmids encoding GFP–Sec61b or H1B–GFP were transfected into U2OS cells. At 18–24 h post transfection, cells were either fixed directly (Unextracted) or after digitonin extraction (Extracted). GFP–Sec61b or H1B–GFP mRNAs were stained with FISH probes against the GFP-coding sequence and visualized. mRNAs in unextracted and digitonin-extracted cells are shown in D. Note that GFP–Sec61b, but not H1B–GFP mRNA, is resistant to digitonin extraction and exhibits a reticular staining pattern. (E) Distribution of GFP–Sec61β protein and mRNA in a digitonin-extracted U2OS cell. Both images are from a single field of view. Note the extensive colocalization of the mRNA with its encoded protein, which is localized to the ER (Rolls et al., 1999; Shibata et al., 2008). (F) Quantification of GFP–Sec61b and H1B–GFP mRNA cytoplasmic intensity signals. The ratio of fluorescence in the cytoplasms of extracted versus unextracted cells was determined. Each bar in C and F represents the mean±s.e.m. of three independent experiments, each containing at least 30 cells. Scale bars: 20 µm.