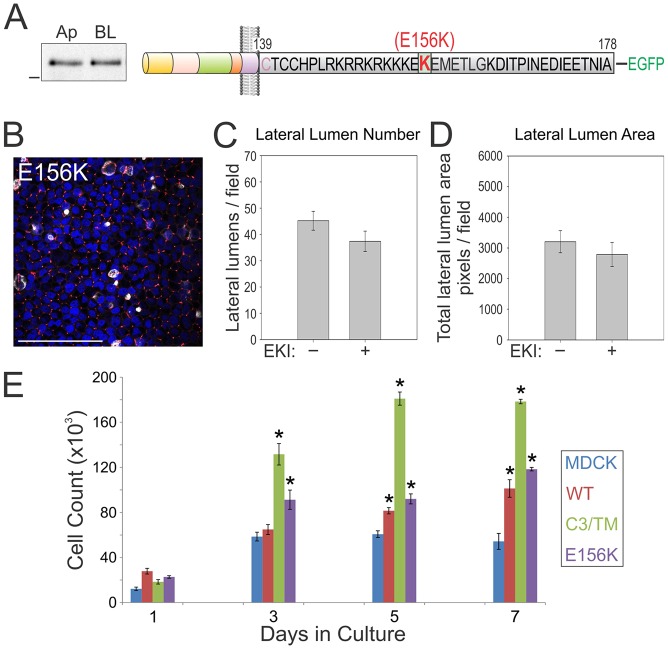
Fig. 8.
A human cancer-associated somatic mutation in the BTC basolateral-sorting motif compromises basolateral trafficking. (A) The E156K BTC mutation that is associated with human pathology was generated within the full-length human BTC protein and fused with EGFP at its C-terminus (top schematic). The relative abundance of the E156K mutant at the apical (Ap) or basolateral (BL) cell surface, as determined by using selective cell-surface biotinylation, is depicted on the left. (B) MDCK cells stably expressing E156K BTC were polarized on Transwell filters, and then fixed and stained with DAPI (blue), and for gp135 (white) and ZO-1 (red). Scale bar: 100 µm. (C,D) E156K-expressing polarized MDCK cells were treated with EKI-785 (EKI) as in Fig. 6. Quantification of number (C) and area (D) of lateral lumens. (E) One hundred thousand MDCK cells stably expressing the indicated BTC–EGFP constructs were plated on Transwell filters in triplicate and counted at the indicated time points. Data are plotted as mean±s.e.m.; *statistically significant difference (P<0.05, two-tailed unpaired t-test) compared with parental MDCK cells. WT, wild type.