Abstract
Background
Molecular genetic mechanisms underlying the anti-inflammatory effects of ethanol extract (GB) from G. bimaculatus, a type of cricket, are not fully elucidated. G. bimaculatus was reported to be rich in unsaturated fatty acid and to decrease the omega-6/omega-3 fatty acid ratio when fed to chickens. GB may reduce the amount of fat or increase the unsaturated fatty acid ratio.
Methods
Male Wistar rats fed a high-fat diet (HFD) were orally administered with 5 groups: phosphate buffered saline (PBS, control), GB (100 mg/kg or 200 mg/kg), Pravastatin or Isaria sinclairii (IS) extract, which is reported to have fat-reducing effects, for either 1 or 2 months. GB’s sero-biochemial, hematological and anti-oxidizing hepato-cellular biomarker levels were evaluated to dertermine their antilipidemic, anti-inflammatory, and anti-coagulant effect in rats after 1 or 2 month GB treatments on HFD (fat 60 %) Wistar rat. The abdominal and epididymidal fat weight were measured and the composition of fatty acid was analyzed by GC/MS. Microarray analyses were performed with a rat 28 K cDNA clone set array to identify the gene-expression profiles for the GB exposed high fat dieted Wistar rat.
Results
The weight and fatty acid composition of abdominal fat and epididymidal fat, total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, and triglyceride in GB treated rats were at lower levels than those of the control group. The anti-oxidant hepato-cellular biomarker levels, protein carbonyl content and malondialdehyde concentration in GB treated rats were significantly decreased. Compared to the control, the GB treated rat group (treated at a dose of 100 and 200 mg/kg), had 190 up-regulated genes including Gpm6a (glycoprotein m6a), Tmem14a (transmembrane protein 14A) and Fasin (fatty acid synthase), with down-regulated 235 genes including Cc121b (chemokine ligand 21b), Glycan1 (glycosylation dependent cell adhesion moleule, Serpinb1a (serine proteinase inhibitor) and Tcrb (T-cell receptor beta chain).
Conclusion
The data suggest Fasin-related fatty acid synthesis and adipose differentiation related protein (Adfp), which is related to obesity, were upregulated by GB treatment, indicating their potential therapeutic markers for anti-atheriosclerosis or inflammation.
Keywords: Anti- atherosclerosis effect, G. Bimaculatus extract, Wistar rats, 1-month treatments
Background
Obesity is a metabolic disorder and the fundamental cause of other fatal diseases including atherosclerosis, hypertension, diabetes, premature aging and cancer [1]. A high fat diet causes diseases such as obesity and changes the DNA gene expression profile [2–4].
Cricket (Gryllus bimaculatus) water extract is used in Oriental medicine as a crude drug for treating fever and hypertension, and crickets are currently reared as food for pets [5]. The main components of G. bimaculatus are protein (52.81 %), ash (minerals) and fat (21.81 %), including rich essential unsaturated conjugated fatty acids – such as palmitic acid (ω-7, 34.14 %), oleic acid (ω-9, 36.48 %), and linoleic acid (ω-6, 13.58 %) [6]. Water and methanol extracts from crickets were recently found to cause a significant decrease in blood ethanol concentrations by enhancing liver mitochondrial alcohol metabolizing enzymes [7]. The extracts also had protective effects against acute hepatic damage [8].
The fact that G. bimaculatus is abundant in unsaturated fatty acid and decrease of omega-6/omega-3 fatty acid ratio when fed to chickens suggest that G. bimaculatus may reduce fat or increase unsaturated fatty acid ratio in tissues [6]. The antioxidant effect of GB reported in previous studies may relieve the obese state or obese-related disorders. Recent studies report anti-obesity and anti-diabetic effects are Isaria sinclairii (Cicada Dongchunghacho, a fungus cultured on silkworm) [9–11]. Pravastatin (a type of statins), lipid-lowering drug, especially hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase inhibitor, is widely used in the treatment and prevention of atherosclerotic diseases [12]. Therefore, we assessed the effects of GB compared its antilipidemic activity with I. sinclarii ethanol extract or Pravastain as positive controls. In this study, the fatty acid composition in abdominal fat tissue and epididymidal tissue of Wistar rats treated with GB was evaluated and compared to Isaria sinclaii [10] extract (IS100) and pravastatin (STA). A high fat diet (HFD) also can cause oxidative stress and was due to lipid peroxidation (malon dialdehyde increase), protein carbonyl content increase, and DNA damage.
We report the sero-biochemical and DNA micro array study of GB in HFD Wistar rats with regard to preventing oxidative stress to proteins, lipids and DNA. This GB holds great promise for use as an anti-obesity drug to decrease fat accumulation in people on high fat diets and prevent changes in liver fat. We demonstrate the potential efficacy of GB in the treatment of anti-lipidemic effect on a HFD rats to be a protective nutraceutical for atherosclerosis disorders, including circulatory disorders, showing gene expression profile with valuable prognostic marker to identify potential therapeutic targets for atherosclerosis and obesity.
Results
Clinical sign and food consumption
No deaths or adverse clinical signs were apparent due to the ingestion of the G. bimaculatus extract or pravastatin. The level of food consumption was similar in all treated groups during the course of the study (Fig. 1). Mean daily food intake was 26.6 g/kg bw/day.
Fig. 1.
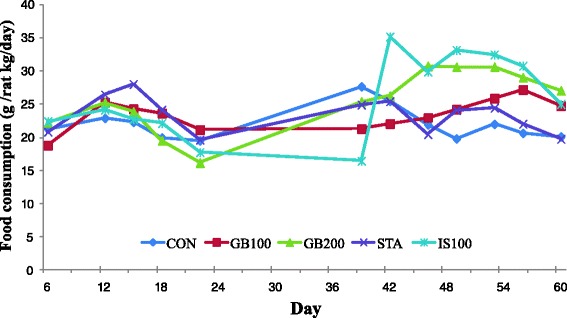
Food consumption changes in Wistar rats treated with GB on a high fat diet
Body weight and adipose fat weight changes
There were no toxicologically significant differences in mean body weight between any of the treatment groups (Fig. 2a). During the 1-month administration period, the body weights of the male Wistar rats in the 2 treatment groups were comparable in the control and trexperimental groups. The mean weekly body weights over time are presented in Fig. 2a. However, about 2 months after the experiment, body weight deviation between the groups increased, especially with the IS100 group. The body weight of the IS100 group continued to decrease for some time. The body weight of the IS100 group was significantly different from that of the control group (p < 0.05). At sacrifice, the abdominal fat tissues and the epididymidal fat tissues were dissected and weighed to investigate adipose tissue changes. The abdominal fat weight of HFD rats was significantly reduced by G. bimaculatus extract (200 mg/kg) (GB200) after 2 months of treatment: Con, 19.16 ± 3.04 g; GB100, 16.37 ± 1.46 (85.4 %); GB 200, 13.03 ± 1.37 g (68.0 %, GB200 vs Con, p < 0.05). Figure 2b also shows the declineof abdominal and epididymidal fat weight in HFD rats treated with GB for 1 month. The relative weight of epididymidal fat tissuedecreased to 75.0 % in GB200 after1 month of treatment. The total fat in GB100 and GB200 decreased by 77.9 and 73 % comparedto the CON (Fig. 2b). The fat-reducing effect of GB extract was better than that of pravastatin (STA) in rats.
Fig. 2.
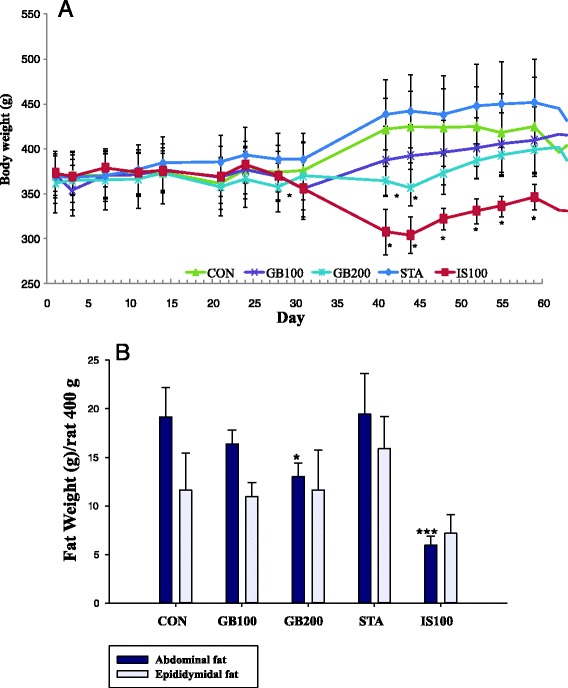
a Effect of GB on body weight in high fat (60 %) dieted rat over 2 months. GB100 (200): G. bimaculatus ethanol extract 100 (200) mg/kg. STA: Pravastatin 2 mg/kg. IS100: I. sinclairii ethanol extract 100 mg/kg. *: significant differences compared with CON group (*p < 0.05). b Effect of GB (1 month treatment) on abdominal and epididymidal fat weight on a high fat diet. *: significant differences compared with CON group (*p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001)
Serum biochemical analysis
The changes in serum lipid and lipoprotein profiles after the 1-mo. feeding period are show in Table 1.
Table 1.
Serological findings for ethanol extract from cricket in Wistar rats on high fat diet over a 1-month treatment period
| Item | Unit | CON | GB100 | STA | IS100 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| phospholipid | mg/dL | 151.50 ± 17.06 | 152.00 ± 19.95 | 178.80 ± 20.20 | 123.40 ± 10.48 |
| FFA | mEq/L | 507.75 ± 45.46 | 465.75 ± 57.94 | 532.40 ± 81.22 | 526.20 ± 126.11 |
| Insulin | mU/ml | <0.2 ± 0.0 | <0.2 ± 0.0 | <0.2 ± 0.0 | <0.2 ± 0.0 |
| Albumin | g/dL | 4.05 ± 0.24 | 3.37 ± 0.21 | 3.94 ± 0.25 | 3.48 ± 0.260 |
| T. Bil | mg/dL | 0.125 ± 0.05 | 0.1 ± 0 | 0.1 ± 0.0 | 0.14 ± 0.09 |
| ALP | IU/L | 133.25 ± 40.46 | 79.75 ± 13.43 | 107.50 ± 63.16 | 168.60 ± 106.11 |
| AST | IU/L | 100.5 ± 14.30 | 143 ± 96.23 | 116.61 ± 9.36 | 168.33 ± 25.0 |
| ALT | IU/L | 41 ± 6.48 | 71.25 ± 67.86 | 49.80 ± 10.23 | 100.80 ± 80.83 |
| IP | mg/dL | 21.48 ± 2.07 | 14.60 ± 2.32a | 14.66 ± 1.34 | 11.14 ± 1.88 |
| yGT | g/dL | <0.3 ± 0.0 | <0.3 ± 0.0 | <0.3 ± 0.0 | <0.3 ± 0.0 |
| CK | IU/L | 257.5 ± 79.37 | 205.50 ± 44.35 | 377.60 ± 88.71 | 236.00 ± 93.74 |
| LDH | IU/L | 1475.25 ± 311.35 | 1206.75 ± 375.44 | 1567.20 ± 344.29 | 1342.00 ± 344.95 |
| Glucose(S) | mg/dL | 340.75 ± 26.48 | 225.00 ± 49.03 | 317.00 ± 85.46 | 213.40 ± 52.18 |
| T. Chol | mg/dL | 105.5 ± 7.33 | 110.25 ± 21.04 | 117.80 ± 22.40 | 83.80 ± 12.28 |
| TG | mg/dL | 167 ± 33.97 | 112.75 ± 20.2 | 151.60 ± 53.35 | 91.80 ± 40.44 |
| LDL Chol | mg/dL | 22.25 ± 4.34 | 32.25 ± 10.37 | 24.80 ± 9.20 | 18.00 ± 6.52 |
| BUN | mg/dL | 23.55 ± 1.25 | 16.2 ± 2.20 | 22.42 ± 2.27 | 27.68 ± 5.18 |
| HDL Chol | mg/dL | 79 ± 7.75 | 73.5 ± 7.05 | 88.20 ± 15.74 | 63.80 ± 12.99 |
| Creatinine | mg/dL | 0.59 ± 0.04 | 0.501 ± 0.09 | 0.61 ± 0.09 | 0.86 ± 0.15 |
| Uric acid | mg/dL | 6.18 ± 1.71 | 5.33 ± 0.22 | 5.48 ± 1.44 | 5.88 ± 0.84 |
| Na | nmol/L | 127.25 ± 4.65 | 133.75 ± 5.68 | 133.40 ± 2.61 | 133.80 ± 2.78 |
| K | nmol/L | 26.78 ± 8.73 | 20.13 ± 4.02 | 21.04 ± 1.85 | 18.86 ± 2.96 |
| Cl | nmol/L | 93.5 ± 2.89 | 95.00 ± 3.16 | 95.20 ± 2.59 | 94.40 ± 2.61 |
| T. protein | g/dL | 6.75 ± 0.5 | 6.35 ± 0.42 | 6.54 ± 0.39 | 6.38 ± 0.47 |
| CRP(HS) | mg/L | 1.68 ± 0.05 | 0.53 ± 0.25 | 1.58 ± 0.40 | 1.16 ± 0.50 |
| Calcium | nmol/L | 12.40 ± 0.64 | 11.90 ± 0.62 | 12.34 ± 0.87 | 12.12 ± 0.40 |
FFA free fatty acid, T. Bil total bilirubin, ALP alkaline phosphatase, AST(GOT) glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase, ALT(GPT) glutamate pyruvate transaminase, IP inorganic phosphorus, GGT γ-glutamyl transferase, CK creatinine phosphokinase, LDH lactate dehydrogenase, Na Sodium, K potassium, Cl chloride, BUN blood urea nitrogen, T. Chol total cholesterol, TG triglyceride, H. Chol high cholesterol, l.Chol low cholesterol, Ca calcium, CRP c-reactive protein
Each value represents mean ± S.D. Statistically significant from control (* P < 0.05)
CON: PBS (vehicle) treated with murine high fat diet
The data obtained clearly show that high-fat diet ingestion increased the concentration of serum triglyceride and serum triglyceride was decreased in the GB100 experimental rats [control, 167.00 ± 33.97 mg/dL; GB100, 112.75 ± 20.2 mg/dL (GB100 vs Con p < 0.05); STA, 151.60 ± 53.35 mg/dL]. Serum glucose levels were lower in the GB-treated group than in the control Serum glucose levels were lower in the GB-treated group than in the control (control, 340.75 ± 26.48 mg/dL; GB100, 225.00 ± 49.03 mg/dL (GB100 vs Con, p < 0.05); Provastastin (STA), 317.00 ± 85.46 mg/dL; IS100, 213.40 ± 52.18 mg/dL). Analysis of C-reactive protein (CRP) levels showed meaningful anti-edema effect with the inhibition of CRP, but the results had no significance (control, 1.68 ± 0.05 mg/L; GB100, 0.53 ± 0.25 mg/L; STA, 1.58 ± 0.40 mg/L; IS100, 1.16 ± 0.5 mg/L). Also, in the sera of GB100-treated rats, free fatty acid (FFA) levels were lower than in the control (control 507.75 ± 4.46 mEq/L; GB100, 465.75 ± 57.094 mEq/L; STA, 532.40 ± 81.22 mEq/L; IS100 526.20 ± 126.11 mEq/L). Triglyceride levels were significantly lower in the GB treated rats compared to the control as follows: control, 167.0 ± 33.97 mg/dL; GB100, 112.75 ± 20.2 mg/dL (GB100 vs CON, p < 0.05); STA, 151.60 ± 53.35 mg/dL; IS100, 91.80 ± 40.44 mg/dL. The alkaline phosphatase (ALP) levels of the treated groups were lower in the high fat diet fed rats (control, 133.25 ± 40.46; GB100, 79.75 ± 13.43 (control, 133.25 ± 40.46 IU/L; GB100, 79.75 ± 13.43 IU/L (GB100 vs CON, p < 0.05); STA, 107.50 ± 63.16 IU/L; IS100, 168.60 ± 106.11 IU/L.
The changes in serum lipid and lipoprotein profiles in HFD rats after GB 2 months of treatment are show in Table 2.
Table 2.
Serological findings for GB in Wistar rats on high fat diet over a 2-month treatment period
| Item | Unit | CON | GB100 | GB200 | STA | IS100 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total protein | g/dL | 6.63 ± 0.18 | 6.75 ± 0.55 | 6.95 ± 0.18 | 6.84 ± 0.15 | 7.00 ± 0.11 |
| Bilirubin | mg/dL | below 0.1 | below 0.1 | below 0.1 | below 0.1 | below 0.1 |
| ALP | U/L | 38.67 ± 4.73 | 38.00 ± 4.24 | 42.75 ± 7.14 | 39.00 ± 3.16 | 42.75 ± 8.26 |
| AST | U/L | 145.00 ± 28.58 | 128.50 ± 21.92 | 144.00 ± 98.18 | 96.60 ± 18.23 | 122.50 ± 51.86 |
| ALT | U/L | 46.67 ± 1.53 | 47.50 ± 10.61 | 81.75 ± 33.31 | 36.60 ± 13.13 | 28.50 ± 4.36 |
| GGT | U/L | below 3 | below 3 | below 3 | below 3 | below 3 |
| CK | U/L | 607.00 ± 188.07 | 438.00 ± 61.00 | 676.25 ± 203.71 | 382.00 ± 36.56 | 256.00 ± 37.45 |
| LDH | U/L | 1577.33 ± 241.14 | 1830.50 ± 281.50 | 1897.25 ± 273.26 | 1179.00 ± 202.53 | 916.50 ± 93.39 |
| Na | mmol/L | 148.50 ± 1.32 | 151.50 ± 1.50 | 147.75 ± 1.31 | 147.40 ± 0.40 | 145.25 ± 0.85 |
| K | mmol/L | 11.20 ± 1.19 | 9.40 ± 2.40 | 10.68 ± 1.18 | 9.24 ± 0.95 | 10.43 ± 0.81 |
| Cl | mmol/L | 97.00 ± 1.08 | 99.00 ± 3.00 | 96.75 ± 1.49 | 98.40 ± 0.87 | 97.25 ± 1.03 |
| Creatine | mg/dL | 0.80 ± 0.03 | 0.69 ± 0.12 | 0.79 ± 0.05 | 0.72 ± 0.03 | 0.92 ± 0.06 |
| BUN | mg/dL | 16.57 ± 0.27 | 17.00 ± 0.00 | 19.78 ± 1.29 | 13.92 ± 0.46 | 25.73 ± 2.41 |
| Uric acid | mg/dL | 3.83 ± 0.48 | 7.85 ± 0.55 | 6.53 ± 0.47 | 6.08 ± 0.56 | 5.90 ± 0.33 |
| T.Chol | mg/dL | 106.00 ± 8.08 | 110.50 ± 24.50 | 93.00 ± 3.61 | 84.40 ± 3.37 | 100.75 ± 8.00 |
| H.Chol | mg/dL | 89.67 ± 6.17 | 95.50 ± 18.50 | 79.67 ± 2.40 | 74.60 ± 2.58 | 89.25 ± 6.16 |
| L.Chol | mg/dL | 21.00 ± 2.00 | 21.00 ± 17.67 | 17.67 ± 0.67 | 15.60 ± 0.81 | 20.00 ± 2.12 |
| TG | mg/dL | 100.50 ± 11.86 | 100.50 ± 0.50 | 101.33 ± 20.02 | 87.20 ± 9.25 | 54.25 ± 4.01 |
| Glucose | mg/dL | 187.67 ± 2.19 | 163.00 ± 18.00 | 192.75 ± 67.45 | 252.00 ± 29.43 | 198.75 ± 30.38 |
| Ca | mg/dL | 11.57 ± 0.07 | 11.70 ± 0.70 | 12.05 ± 0.37 | 12.30 ± 0.42 | 12.53 ± 0.37 |
| IP | mg/dL | 21.10 ± 1.07 | 19.25 ± 2.25 | 19.68 ± 1.77 | 14.44 ± 1.60 | 11.18 ± 0.85 |
| FFA | uEq/L | 907.49 ± 191.70 | 1071.50 ± 42.50 | 931.00 ± 81.12 | 855.00 ± 122.43 | 738.00 ± 51.22 |
Each value represents mean ± S.E. statistically significant from control (* P < 0.05)
The obtained data clearly show that high-fat diet consumption increased the concentration of serum total cholesterol, TG, and LDL-cholesterol in addition to decreasing the HDL-cholesterol concentrations in the experimental rats after 2 months of treatment. Total cholesterol, LDL- cholesterol, TG, and total lipid in the GB-treated group were lower than in the control group. HDL-cholesterol in the GB-treated group was higher than in the control group.
Serum glucose levels were lower in the GB-treated group than in the control (control, 187.67 ± 2.19 mg/dL; GB100, 163.00 ± 18.00 mg/dL; GB200, 192.75 ± 67.45 mg/dL; STA, 252.00 ± 29.43 mg/dL (STA vs CON, p < 0.05); IS100, 198.75 ± 30.38 mg/dL). In the sera of the GB treated groups, total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol and triglyceride levels were lower, while HDL-cholesterol was higher than in the control after 2 months. Dose-dependent changes were observed in rats on high-fat diets although there were no significant differences compared with the control group (Fig. 3).
Fig. 3.
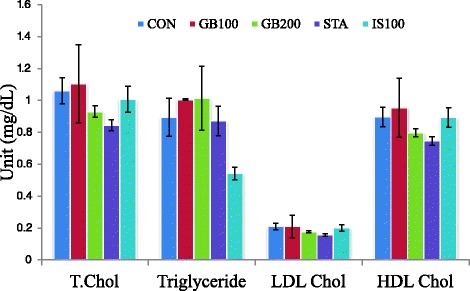
Effect of GB on serum total cholesterol, triglyceride and HDL-cholesterol level in High fat diet rats (2 month GB treatment)
Hematology and blood chemical analysis
Some dose-dependent changes were observed between the treated and control groups with respect to the hematological parameters at the end of the experiment. An increase in partial thromboplastin time and thrombin time was observed in the treated groups on high fat diets but without significant differences. Minor changes were found in hematological parameters (hematocrit, MCV, MCHC and factor I) for some GB-treated rat groups. However, the effects of GB were not considered adverse because all changes in hematological data including neutrophil, lymphocyte, monocyte and eosinophil were within the normal physiological range. The platelet count of the IS100 group was increased compared to the CON group (p < 0.05) (Table 3).
Table 3.
Hematological findings for extract from cricket in Wistar rats on high fat diet over a 2-month treatment period
| Unit | CON | GB100 | GB200 | STA | IS100 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WBC | 103/μl | 535 ± 0.54 | 6.67 ± 1.56 | 6.28 ± 0.75 | 4.60 ± 0.35 | 7.3 ± 0.56 |
| RBC | 10μl | 8.15 ± 0.09 | 8.65 ± 0.71 | 9.04 ± 0.20 | 8.83 ± 0.19 | 8.56 ± 0.11 |
| Hgb | g/dL | 1496 ± 0.29 | 15.10 ± 0.50 | 15.75 ± 0.22 | 15.78 ± 0.20 | 14.83 ± 0.09 |
| Hct | % | 50.16 ± 1.01 | 51.50 ± 2.60 | 53.68 ± 0.88 | 53.26 ± 0.76 | 49.65 ± 0.43 |
| MCV | fL | 6156 ± 1.15 | 59.70 ± 1.90 | 59.43 ± 0.72 | 60.40 ± 0.76 | 58.03 ± 0.95 |
| MCH | pg | 18.18 ± 0.49 | 17.55 ± 0.85 | 17.40 ± 0.36 | 17.92 ± 0.24 | 17.30 ± 0.30 |
| MCHC | g/dL | 29.84 ± 0.25 | 29.35 ± 0.45 | 29.30 ± 0.27 | 29.64 ± 0.16 | 29.85 ± 0.14 |
| PLT | 103/μl | 974.00 ± 67.06 | 938.50 ± 216.50 | 1044.00 ± 63.44 | 954.80 ± 38.77 | 1240.25 ± 24.32 |
| PTT | sec | 98.06 ± 18.58 | 107.80 ± 36.20 | 76.03 ± 11.13 | 74.70 ± 7.26 | 59.50 ± 12.03 |
| Thrombin time | sec | 60.10 ± 13.69 | 63.40 ± 22.10 | 53.40 ± 11.06 | 47.70 ± 6.08 | 50.90 ± 9.49 |
| Factor I | mg/dL | 194.00 ± 3012 | 216.50 ± 9.50 | 245.75 ± 18.36 | 214.60 ± 26.21 | 247.75 ± 13.03 |
| PT | sce | 5.66 ± 0.16 | 1.59 ± 0.11 | 1.53 ± 0.04 | 1.48 ± 0.06 | 1.46 ± 0.07 |
| Neutrophil | % | 21.70 ± 334 | 13.10 ± 0.60 | 16.83 ± 2.28 | 16.72 ± 1.66 | 18.23 ± 1.89 |
| Lymphocyte | % | 75.43 ± UJ oo | 85.55 ± 0.55 | 81.48 ± 2.49 | 81.22 ± 1.84 | 79.78 ± 2.08 |
| Monocyte | % | 0.90 ± 0.19 | 0.35 ± 0.05 | 0.43 ± 0.14 | 0.64 ± 0.10 | 0.68 ± 0.19 |
| Eosinophil | % | 1.62 ± 0.13 | 0.85 ± 0.05 | 1.03 ± 0.13 | 1.04 ± 0.15 | 0.88 ± 0.08 |
| Basophil | % | 0.34 ± 0.08 | 0.15 ± 0.05 | 0.25 ± 0.06 | 0.38 ± 0.07 | 158 ± 1.14 |
WBC white blood cell, RBC red blood cell, Hgb hemoglobin, Hct hematocrit, MCV mean corpuscular volume, MCH mean corpuscular hemoglobin, MCHC mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration, PLT partial thromboplastin time, PT prothrombin time
CON: PBS (as a vehicle) treated with high fat diet
Each value represents mean ± S.E. Statistically significant from control (P* < 0.05)
Oxidative protein damage (carbonyl content and catalase) quantitation
Protein oxidative stress was evaluated by measuring protein carbonyl content in the blood (Fig. 4). Catalase activity and carbonyl content were assayed as the biomarkers of protein oxidative damage in the high fat dieted rat model.
Fig. 4.
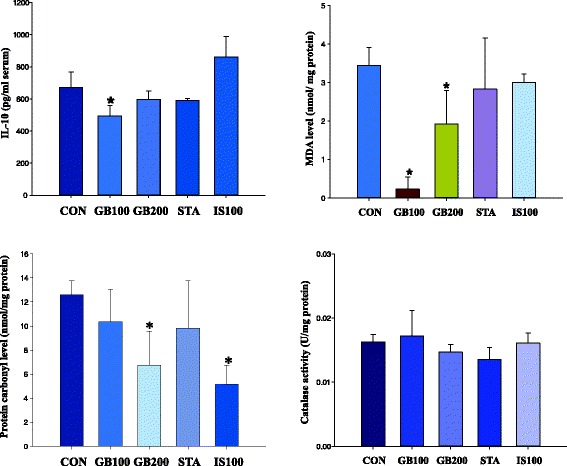
Anti-oxidative effect of GB on lipids (MDA or IL-6) and proteins (carbonyl or catalase content) after 2-month treatment. Each value represents mean ± S.D. statistically significant from control (*P < 0.05)
After 2 months, carbonyl content level was decreased by GB treatment: CON, 12.6 ± 1.1 nmol/mg protein; GB100, 10.4 ± 2.7 nmol/mg protein; GB200 (GB200 vs CON, P < 0.05), 6.8 ± 2.8 nmol/mg protein; STA, 9.8 ± 4.0 nmol/mg protein; IS100, 5.1 ± 1.6 nmol/mg protein (IS100 vs CON, P < 0.05). The protein carbonyl content in the blood was reduced in a dose-dependent manner after extract treatments for 2 months. The protein carbonyl concentration was decreased by 82 and 53 % in GB100 and GB200, respectively (Fig. 4).
The catalase activity (Ug/protein) after 2 months of GB treatment was as follows: CON, 0.016 ± 0.001 U/mg protein; GB100, 0.017 ± 0.004 U/mg protein; GB200, 0.014 ± 0.001 U/mg protein; STA (2 mg/kg), 0.014 ± 0.002 U/mg protein; IS100, 0.016 ± 0.002 U/mg protein in hepatocytes (Fig. 4). The catalase activity in all hepatocyte groups was not affected.
Oxidative lipid damage (malondialdehyde) quantitation
As a lipid oxidative damage marker in lipid oxidative stress states, malondialdehyde level (MDA, nmol/mg/protein) was assayed after 2 months of GB treatment: PBS (CON), 3.44 ± 0.47 nmol/mg/protein; GB 100, 0.23 ± 0.31 (GB100 vs CON, p < 0.05) nmol/mg/protein, GB 200, 1.92 ± 0.87 nmol/mg/protein (GB200 vs CON, p < 0.05); STA, 2.83 ± 1.33 nmol/mg/protein; IS100, 3.00 ± 0.22 nmol/mg/protein (Fig. 4). Pravastatin (STA) and IS100 did not affect the lipid peroxidation in hepatocytes.
Cytokine IL-10 production
Decrease of serum IL-10 level was observed in the GB-treated group. IL-10 activity after 2 months of GB treatment in HFD rat serum was as follows: PBS: 670.5 ± 96.1 pg/ml serum, GB 100: 492.0 ± 66.6 pg/ml serum (GB100 vs CON, p < 0.05), GB 200: 598.1 ± 51.8 pg/ml serum, STA: 590.7 ± 12.2 pg/ml serum, IS100: 862.4 ± 126.6 pg/ml serum (Fig. 4). STA and IS100 had no statistical differences compared with the CON group.
DNA microarray
Microarray analysis using a Mouse 28 K cDNA clone set array was performed to identify the gene-expression profiles in the GB treated Wistar rat livers and provided information on potential markers for atherosclerosis. Compared to the control group, the GB treated rats showed 419 (200 mg/kg) and 430 (100 mg/kg) up-regulated genes (15 % increase), and the signal ratio increased from 1.15-fold to 3.28-fold. Gpm6a (glycoprotein m6a), Tmem14a (transmembrane protein 14A) and Fasin (fatty acid synthase) were up-regulated and 421 genes (ratio 0.47 ~ 0.85) including Cc121b (chemokine ligand 21b), Glycan1 (glycosylation dependent cell adhesion moleule, Serpinb1a (serine proteinase inhibitor) and Tcrb (T-cell receptor beta chain) were down-regulated. The data suggests that Fasin related fatty acid synthesis and Adfp, an adipose differentiation related protein associated with obesity, were upregulated by GB treatment. However, a series of genes involved in signal transduction, fatty acid synthesis, energy metabolism (oxidative metabolism) and cellular defenses were more up-regulated, indicating their potential as therapeutic markers for lipid metabolism (Tables 4 and 5).
Table 4.
Upregulated genes differentially expressed in liver tissue of high fat diet rats treated with G. bimaculatus extract over a 1-month period
| G100a | G200b | Gene title | Gene symbol | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.891 | 1.916 | glycoprotein m6a | Gpm6a |
| 2 | 0.957 | 1.767 | transmembrane protein 14A | Tmem14a |
| 3 | 1.300 | 1.416 | fatty acid synthase | Fasn |
| 4 | 0.993 | 1.396 | RT1 class I, locus CE5 | RT1-CE5 |
| 5 | 1.370 | 1.393 | ubiquitin-like modifier activating enzyme 5 | Uba5 |
| 6 | 0.617 | 1.372 | RT1 class Ib, locus EC2 | RT1-EC2 |
| 7 | 1.101 | 1.358 | TWIST neighbor | Twistnb |
| 8 | 1.303 | 1.345 | coagulation factor C homolog, cochlin | Coch |
| 9 | 1.497 | 1.343 | X-linked Kx blood group (McLeod syndrome) homolog | Xk |
| 10 | 1.171 | 1.341 | dedicator of cytokinesis 11 | Dock11 |
| 11 | 0.945 | 1.335 | amyloid beta (A4) precursor-like protein 1 | Aplp1 |
| 12 | 0.853 | 1.334 | D site of albumin promoter binding protein | Dbp |
| 13 | 0.794 | 1.326 | RT1 class I, locus CE11-like /// RT1 class I, locus A3 | LOC100364500 |
| 14 | 1.860 | 1.319 | Sumo1/sentrin/SMT3 specific peptidase 5 | Senp5 |
| 15 | 1.125 | 1.316 | platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase, isoform 1b | Pafah1b1 |
| 16 | 1.032 | 1.306 | isoprenoid synthase domain containing | Ispd |
| 17 | 1.163 | 1.288 | osteoglycin | Ogn |
| 18 | 1.273 | 1.280 | myxovirus (influenza virus) resistance 2 | Mx2 |
| 19 | 0.957 | 1.276 | similar to KIAA0802 protein | RGD1308319 |
| 20 | 1.170 | 1.276 | echinoderm microtubule associated protein like 2 | Eml2 |
| 21 | 1.061 | 1.275 | Rab40b, member RAS oncogene family | Rab40b |
| 22 | 1.099 | 1.268 | Complement component 1, q subcomponent-like 3 | C1ql3 |
| 23 | 1.399 | 1.266 | family with sequence similarity 135, member A | Fam135a |
| 24 | 1.377 | 1.266 | Adipose differentiation related protein | Adfp |
| 25 | 1.091 | 1.264 | acylphosphatase 2, muscle type | Acyp2 |
| 26 | 1.058 | 1.259 | RAD23 homolog B (S. cerevisiae) | Rad23b |
| 27 | 1.141 | 1.258 | cytochrome P450, family 4, subfamily v, polypeptide 3 | Cyp4v3 |
| 28 | 1.113 | 1.256 | Opticin | Optc |
| 29 | 0.961 | 1.255 | ubiquitin D | Ubd |
| 30 | 1.038 | 1.253 | nucleosome assembly protein 1-like 3 | Nap1l3 |
| 31 | 1.168 | 1.252 | protocadherin alpha 1 /// protocadherin alpha 10 | Pcdha1 |
| 32 | 1.183 | 1.251 | similar to CG12279-PA | LOC500420 |
| 33 | 1.058 | 1.249 | solute carrier family 31 (copper transporters), member 1 | Slc31a1 |
| 34 | 0.979 | 1.248 | stem-loop binding protein | Slbp |
| 35 | 1.026 | 1.242 | O-sialoglycoprotein endopeptidase-like 1 | Osgepl1 |
| 36 | 1.060 | 1.240 | ring finger protein 141 | rnf141 |
| 37 | 1.006 | 1.240 | caveolin 2 /// caveolin 2-like | Cav2 |
| 38 | 1.025 | 1.240 | major facilitator superfamily domain containing 9 | Mfsd9 |
| 39 | 0.991 | 1.238 | chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 9 | Cxcl9 |
| 40 | 1.237 | 1.237 | protein phosphatase 4, regulatory subunit 2 | Ppp4r2 |
aGB100/control ratio
bGB200/control ratio
Table 5.
Downregulated genes differentially expressed in liver tissue of high fat diet rats treated with GB over a 1-month period
| GB100a | GB200b | Gene title | Gene symbol | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.478 | 0.472 | chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 21b | Ccl21b |
| 2 | 0.563 | 0.563 | glycosylation dependent cell adhesion molecule 1 | Glycam1 |
| 3 | 0.610 | 0.583 | serine (or cysteine) proteinase inhibitor, clade B, member Serpinb1a | |
| 4 | 0.625 | 0.599 | T-cell receptor beta chain | Tcrb |
| 5 | 0.755 | 0.618 | Lymphoid enhancer binding factor 1 | Lef1 |
| 6 | 0.615 | 0.646 | T-cell receptor beta chain | Tcrb |
| 7 | 0.646 | 0.658 | immunoglobulin heavy chain 6 | Igh-6 |
| 8 | 0.699 | 0.658 | CD3 molecule, gamma polypeptide | Cd3g |
| 9 | 0.680 | 0.680 | coronin, actin binding protein 1A | Coro1a |
| 10 | 0.687 | 0.687 | SATB homeobox 1 | Satb1 |
| 11 | 0.623 | 0.695 | similar to RIKEN cDNA A430107P09 | LOC100364854 |
| 12 | 0.717 | 0.701 | Fas apoptotic inhibitory molecule 3 | Faim3 |
| 13 | 0.703 | 0.715 | lumican | Lum |
| 14 | 0.924 | 0.722 | interleukin 7 receptor | Il7r |
| 15 | 0.815 | 0.731 | SATB homeobox 1 | Satb1 |
| 16 | 0.869 | 0.740 | CD3 molecule, epsilon polypeptide | Cd3e |
| 17 | 0.819 | 0.742 | ADP-ribosylation factor-like 5C | Arl5c |
| 18 | 0.749 | 0.749 | protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, C | Ptprc |
| 19 | 0.889 | 0.755 | cancer susceptibility candidate 1 | Casc1 |
| 20 | 0.879 | 0.758 | LIM domain containing 2 | Limd2 |
| 21 | 0.901 | 0.760 | bromodomain containing 4 | Brd4 |
| 22 | 1.007 | 0.764 | proenkephalin | Penk |
| 23 | 0.776 | 0.765 | hypothetical protein LOC100364588 | LOC100364588 |
| 24 | 0.915 | 0.768 | phospholipase D1 | Pld1 |
| 25 | 0.777 | 0.769 | immunoglobulin joining chain | Igj |
| 26 | 0.941 | 0.769 | sodium channel, voltage-gated, type IV, alpha subunit | Scn4a |
| 27 | 0.806 | 0.770 | Zinc finger protein 710 | Znf710 |
| 28 | 0.729 | 0.770 | thyroid hormone receptor beta | Thrb |
| 29 | 0.926 | 0.774 | transition protein 2 | Tnp2 |
| 30 | 0.822 | 0.774 | SWI/SNF-related matrix-aa-dependent regulator of c2 | LOC685179 |
| 31 | 0.958 | 0.774 | protocadherin gamma subfamily A, 1 | Pcdhga1 |
| 32 | 0.821 | 0.776 | tubulin, beta 2c | Tubb2c |
| 33 | 0.938 | 0.776 | galanin receptor 2 | Galr2 |
| 34 | 0.838 | 0.777 | matrix metallopeptidase 12 | Mmp12 |
| 35 | 0.777 | 0.777 | SAM and SH3 domain containing 3 | Sash3 |
| 36 | 0.771 | 0.777 | TBC1 domain family, member 10C | Tbc1d10c |
| 37 | 0.981 | 0.779 | 2′-5′-oligoadenylate synthetase-like | Oasl |
| 38 | 0.764 | 0.779 | similar to immunoglobulin light chain variable region | RGD1564318 |
| 39 | 0.812 | 0.779 | POU class 2 associating factor 1 | Pou2af1 |
| 40 | 0.783 | 0.783 | CD3 molecule delta polypeptide | Cd3d |
aGB100/control ratio
bGB200/control ratio
Fatty acid composition in adipose tissue
The fatty acid profile, as indicated GC-MS, showed a slight dose-dependent increase in arachidonic acid (C20: 4n6, AFA) concentration in the epididymidal of male Wistar rats in the GB- treated groups over a 2-month period compared to the control group (Table 6). The high fat dieted Wistar rats treated with GB showed increases in the unsaturated fatty acids (FA) ratio, especially single (mono) FA, but had decreases in saturated fatty acid (Tables 6 and 7).
Table 6.
Analysis of fatty acid composition in abdominal fat of Wistar rats on high fat diets treated with G. bimaculatus extract for 1 month
| Comp. of abdominal fat tissue (%) | PBS | GB100 | GB200 | STA | IS100 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lauric acid (C12:0) | 0.04 ± 0.00 | 0.05 ± 0.00* | 0.05 ± 0.00 | 0.05 ± 0.00* | 0.04 ± 0.00 |
| Myristoleic acid (C14:1) | 0.02 ± 0.00 | 0.02 ± 0.00 | 0.02 ± 0.00* | 0.02 ± 0.00 | 0.02 ± 0.00 |
| Myristic acid (C14:0) | 0.72 ± 0.03 | 0.74 ± 0.04 | 0.64 ± 0.13 | 0.66 ± 0.02 | 0.69 ± 0.01 |
| Pentadecanoic acid (C15:0) | 0.12 ± 0.00 | 0.12 ± 0.00 | 0.24 ± 0.12 | 0.12 ± 0.00 | 0.12 ± 0.01 |
| Palmitoleic acid (C16:1) | 1.37 ± 0.14 | 1.52 ± 0.22 | 1.76 ± 0.07* | 1.18 ± 0.17 | 1.31 ± 0.04 |
| Palmitic acid (C16:0) | 21.49 ± 0.49 | 21.42 ± 0.59 | 21.46 ± 0.39 | 21.20 ± 0.14 | 20.85 ± 0.17 |
| Heptadecanoic acid (C17:0) | 0.29 ± 0.01 | 0.28 ± 0.01 | 0.29 ± 0.01 | 0.33 ± 0.01* | 0.30 ± 0.01 |
| Linoleic acid (C18:2) | 34.37 ± 2.80 | 35.24 ± 0.91 | 35.50 ± 0.27 | 31.56 ± 0.92 | 34.70 ± 0.90 |
| Oleic acid (C18:1) | 33.56 ± 2.35 | 32.94 ± 0.89 | 32.33 ± 0.57 | 35.84 ± 0.88 | 33.79 ± 0.89 |
| Stearic acid (C18:0) | 6.92 ± 0.13 | 6.72 ± 0.37 | 6.75 ± 0.17 | 7.90 ± 0.21* | 7.09 ± 0.20 |
| Arachidonic acid (C20:4) | 0.20 ± 0.06 | 0.14 ± 0.02 | 0.13 ± 0.01 | 0.19 ± 0.00 | 0.19 ± 0.04 |
| Eicosapentaenoic acid (C20:5) | 0.02 ± 0.00 | 0.02 ± 0.00 | 0.02 ± 0.00 | 0.03 ± 0.00 | 0.01 ± 0.00 |
| Eicosatrienoic acid (C20:3) | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 0.05 ± 0.00 | 0.06 ± 0.00 | 0.06 ± 0.01 |
| Eicosadienoic acid (C20:2) | 0.25 ± 0.00 | 0.25 ± 0.03 | 0.24 ± 0.01 | 0.29 ± 0.00* | 0.24 ± 0.01 |
| Eicosenoic acid (C20:1) | 0.37 ± 0.01 | 0.38 ± 0.04 | 0.39 ± 0.01 | 0.43 ± 0.01* | 0.41 ± 0.01 |
| Eicosanoic acid (C20:0) | 0.09 ± 0.01 | 0.09 ± 0.01 | 0.09 ± 0.01 | 0.10 ± 0.00 | 0.10 ± 0.01 |
| Docosahexaenoic acid (C22:6) | 0.11 ± 0.08 | 0.04 ± 0.00 | 0.04 ± 0.00 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.09 ± 0.04 |
| Saturated fatty acid | 29.66 ± 0.59 | 29.41 ± 0.39 | 29.52 ± 0.40 | 30.36 ± 0.18 | 29.19 ± 0.28 |
| Unsaturated fatty acid | 70.34 ± 0.59 | 70.59 ± 0.39 | 70.48 ± 0.40 | 69.64 ± 0.18 | 70.81 ± 0.28 |
| Single unsaturated fatty acid | 35.33 ± 1.06 | 34.86 ± 1.22 | 34.50 ± 2.53 | 37.47 ± 2.23 | 35.52 ± 0.42 |
| Poly unsaturated fatty acid | 35.02 ± 2.73 | 35.73 ± 0.88 | 35.98 ± 0.29 | 32.16 ± 0.93 | 35.29 ± 0.93 |
| Comp. of epididymidal fat tissue (%) | PBS | GB100 | GB200 | STA | IS100 |
| Lauric acid (C12:0) | 0.04 ± 0.00 | 0.04 ± 0.00 | 0.04 ± 0.00 | 0.05 ± 0.00 | 0.04 ± 0.00 |
| Myristoleic acid (C14:1) | 0.02 ± 0.00 | 0.03 ± 0.00 | 0.03 ± 0.00 | 0.03 ± 0.00 | 0.03 ± 0.00 |
| Myristic acid (C14:0) | 0.70 ± 0.04 | 0.78 ± 0.02 | 0.74 ± 0.01 | 0.75 ± 0.01 | 0.73 ± 0.03 |
| Pentadecanoic acid (C15:0) | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 0.14 ± 0.01 | 0.14 ± 0.00* | 0.13 ± 0.00 | 0.14 ± 0.01 |
| Palmitoleic acid (C16:1) | 1.66 ± 0.15 | 1.77 ± 0.07 | 1.83 ± 0.05 | 1.76 ± 0.06 | 1.73 ± 0.11 |
| Palmitic acid (C16:0) | 21.89 ± 0.40 | 21.82 ± 0.17 | 21.95 ± 0.21 | 20.66 ± 0.20* | 20.73 ± 0.12 |
| Heptadecanoic acid (C17:0) | 0.26 ± 0.01 | 0.27 ± 0.01 | 0.27 ± 0.00 | 0.28 ± 0.01 | 0.28 ± 0.01 |
| Linoleic acid (C18:2) | 36.05 ± 0.96 | 38.21 ± 1.19 | 37.86 ± 0.60 | 39.68 ± 1.24* | 38.29 ± 0.08 |
| Oleic acid (C18:1) | 32.41 ± 0.65 | 30.19 ± 1.23 | 30.69 ± 0.52 | 29.48 ± 1.00* | 31.27 ± 0.27 |
| Stearic acid (C18:0) | 5.94 ± 0.07 | 5.87 ± 0.09 | 5.57 ± 0.07* | 6.14 ± 0.13 | 5.75 ± 0.03 |
| Arachidonic acid (C20:4) | 0.16 ± 0.01 | 0.13 ± 0.03 | 0.15 ± 0.00 | 0.21 ± 0.03 | 0.19 ± 0.01 |
| Eicosapentaenoic acid (C20:5) | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.03 ± 0.00* | 0.03 ± 0.00* | 0.03 ± 0.00 |
| Eicosatrienoic acid (C20:3) | 0.06 ± 0.00 | 0.06 ± 0.00 | 0.05 ± 0.00 | 0.07 ± 0.00 | 0.07 ± 0.01 |
| Eicosadienoic acid (C20:2) | 0.25 ± 0.01 | 0.25 ± 0.01 | 0.23 ± 0.01 | 0.28 ± 0.01 | 0.27 ± 0.02 |
| Eicosenoic acid (C20:1) | 0.33 ± 0.01 | 0.32 ± 0.01 | 0.30 ± 0.00* | 0.34 ± 0.01 | 0.33 ± 0.01 |
| Eicosanoic acid (C20:0) | 0.06 ± 0.00 | 0.06 ± 0.00 | 0.06 ± 0.00 | 0.06 ± 0.00 | 0.05 ± 0.00 |
| Docosahexaenoic acid (C22:6) | 0.03 ± 0.00 | 0.04 ± 0.00 | 0.06 ± 0.00* | 0.06 ± 0.02 | 0.07 ± 0.00* |
| Saturated fatty acid | 29.01 ± 0.38 | 28.98 ± 0.18 | 28.76 ± 0.16 | 28.06 ± 0.32 | 27.71 ± 0.16 |
| Unsaturated fatty acid | 70.99 ± 0.38 | 71.02 ± 0.18 | 71.24 ± 0.16 | 71.94 ± 0.32 | 72.29 ± 0.16 |
| Single unsaturated fatty acid | 34.42 ± 0.71 | 32.32 ± 1.26 | 32.86 ± 0.54 | 31.61 ± 0.97 | 33.36 ± 0.15 |
| Poly unsaturated fatty acid | 36.57 ± 0.97 | 38.71 ± 1.15 | 38.38 ± 0.59 | 40.33 ± 1.29 | 38.93 ± 0.05 |
Each value represents mean ± SE
Asterisk marks (*) mean significant differences compared with control (PBS) group (p < 0.05)
Table 7.
Analysis of fatty acid composition in abdominal fat of Wistar rats on a high fat diet treated with G. bimaculatus extract for 2 months
| Comp. of abdomianlfat tissue (%) | PBS | GB100 | GB200 | STA | IS100 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lauric acid (C12:0) | 0.04 ± 0.00 | 0.05 ± 0.00 | 0.05 ± 0.00 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.01 |
| Myristoleic acid (C14:1) | 0.02 ± 0.00 | 0.02 ± 0.00 | 0.02 ± 0.00 | 0.02 ± 0.00 | 0.02 ± 0.00 |
| Myristic acid (C14:0) | 0.78 ± 0.04 | 0.77 ± 0.08 | 0.81 ± 0.06 | 0.78 ± 0.01 | 0.88 ± 0.08 |
| Pentadecanoic acid (C15:0) | 0.13 ± 0.00 | 0.14 ± 0.00* | 0.14 ± 0.02 | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 0.15 ± 0.00* |
| Palmitoleic acid (C16:1) | 1.74 ± 0.33 | 1.98 ± 0.22 | 1.93 ± 0.12 | 2.08 ± 0.20 | 1.86 ± 0.23 |
| Palmitic acid (C16:0) | 19.01 ± 0.57 | 18.85 ± 0.61 | 19.85 ± 1.05 | 18.25 ± 0.94 | 19.57 ± 1.27 |
| Heptadecanoic acid (C17:0) | 0.35 ± 0.04 | 0.40 ± 0.03 | 0.46 ± 0.03 | 0.37 ± 0.03 | 0.44 ± 0.03 |
| Linoleic acid (C18:2) | 36.15 ± 1.91 | 40.11 ± 2.23 | 37.26 ± 6.88 | 40.18 ± 0.89 | 38.90 ± 1.91 |
| Oleic acid (C18:1) | 32.10 ± 2.20 | 28.12 ± 0.80 | 28.54 ± 5.66 | 28.88 ± 1.53 | 26.16 ± 1.08 |
| Stearic acid (C18:0) | 8.29 ± 0.45 | 8.35 ± 0.69 | 9.28 ± 0.33 | 7.86 ± 0.69 | 10.16 ± 0.38* |
| Arachidonic acid (C20:4) | 0.20 ± 0.04 | 0.18 ± 0.05 | 0.24 ± 0.02 | 0.24 ± 0.04 | 0.32 ± 0.07 |
| Eicosapentaenoic acid (C20:5) | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.03 ± 0.00 | 0.04 ± 0.00 | 0.03 ± 0.00 | 0.04 ± 0.01 |
| Eicosatrienoic acid (C20:3) | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.02 | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 0.09 ± 0.02 |
| Eicosadienoic acid (C20:2) | 0.35 ± 0.02 | 0.30 ± 0.07 | 0.43 ± 0.03 | 0.35 ± 0.02 | 0.48 ± 0.11 |
| Eicosenoic acid (C20:1) | 0.56 ± 0.02 | 0.49 ± 0.09 | 0.65 ± 0.05 | 0.54 ± 0.01 | 0.69 ± 0.11 |
| Eicosanoic acid (C20:0) | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 0.12 ± 0.02 | 0.15 ± 0.02 |
| Docosahexaenoic acid (C22:6) | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.04 ± 0.00 | 0.07 ± 0.02 | 0.04 ± 0.00 | 0.06 ± 0.00 |
| Saturated fatty acid | 28.73 ± 0.09 | 28.67 ± 1.43 | 30.74 ± 1.16 | 27.57 ± 1.67 | 31.39 ± 1.70 |
| Unsaturated fatty acid | 71.27 ± 0.09 | 71.33 ± 1.43 | 69.26 ± 1.16 | 72.43 ± 1.67 | 68.61 ± 1.70 |
| Single unsaturated fatty acid | 34.42 ± 1.92 | 30.60 ± 0.67 | 31.13 ± 5.71 | 31.51 ± 1.71 | 28.73 ± 0.94 |
| Poly unsaturated fatty acid | 36.84 ± 1.87 | 40.73 ± 2.10 | 38.13 ± 6.86 | 40.92 ± 0.96 | 39.88 ± 1.71 |
| Comp. of epididymidal fat tissue (%) | PBS | GB100 | GB200 | STA | IS100 |
| Lauric acid (C12:0) | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.00 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.00 | 0.09 ± 0.02 |
| Myristoleic acid (C14:1) | 0.04 ± 0.00 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.02 |
| Myristic acid (C14:0) | 1.00 ± 0.10 | 0.90 ± 0.04 | 0.97 ± 0.06 | 0.89 ± 0.06 | 1.03 ± 0.03 |
| Pentadecanoic acid (C15:0) | 0.17 ± 0.01 | 0.19 ± 0.01 | 0.19 ± 0.01 | 0.16 ± 0.01 | 0.19 ± 0.01 |
| Palmitoleic acid (C16:1) | 2.44 ± 0.29 | 3.18 ± 0.92 | 2.61 ± 0.35 | 3.06 ± 0.31 | 2.57 ± 0.47 |
| Palmitic acid (C16:0) | 18.63 ± 0.27 | 18.43 ± 1.41 | 19.53 ± 0.38 | 19.97 ± 0.58 | 18.71 ± 0.72 |
| Heptadecanoic acid (C17:0) | 0.36 ± 0.04 | 0.38 ± 0.05 | 0.41 ± 0.02 | 0.39 ± 0.02 | 0.38 ± 0.03 |
| Linoleic acid (C18:2) | 39.26 ± 1.15 | 39.86 ± 0.98 | 36.49 ± 2.13 | 36.59 ± 1.16 | 34.77 ± 3.41 |
| Oleic acid (C18:1) | 28.85 ± 1.57 | 27.56 ± 0.96 | 29.85 ± 1.81 | 29.92 ± 1.35 | 32.79 ± 3.43 |
| Stearic acid (C18:0) | 7.50 ± 0.22 | 6.96 ± 1.47 | 7.71 ± 0.29 | 7.06 ± 0.41 | 7.44 ± 0.72 |
| Arachidonic acid (C20:4) | 0.32 ± 0.02 | 0.56 ± 0.06* | 0.48 ± 0.07 | 0.40 ± 0.08 | 0.47 ± 0.07 |
| Eicosapentaenoic acid (C20:5) | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 0.08 ± 0.03 | 0.07 ± 0.02 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 0.05 ± 0.02 |
| Eicosatrienoic acid (C20:3) | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 0.17 ± 0.02* | 0.15 ± 0.02 | 0.14 ± 0.02 | 0.15 ± 0.02 |
| Eicosadienoic acid (C20:2) | 0.46 ± 0.01 | 0.51 ± 0.01 | 0.52 ± 0.04 | 0.51 ± 0.02 | 0.46 ± 0.06 |
| Eicosenoic acid (C20:1) | 0.56 ± 0.02 | 0.62 ± 0.07 | 0.58 ± 0.02 | 0.58 ± 0.03 | 0.54 ± 0.09 |
| Eicosanoic acid (C20:0) | 0.09 ± 0.01 | 0.09 ± 0.03 | 0.08 ± 0.00 | 0.09 ± 0.01 | 0.12 ± 0.01* |
| Docosahexaenoic acid (C22:6) | 0.10 ± 0.01 | 0.37 ± 0.08* | 0.24 ± 0.05 | 0.11 ± 0.04 | 0.19 ± 0.06 |
| Saturated fatty acid | 27.80 ± 0.33 | 27.03 ± 3.00 | 28.96 ± 0.66 | 28.61 ± 0.91 | 27.96 ± 1.19 |
| Unsaturated fatty acid | 72.20 ± 0.33 | 72.97 ± 3.00 | 71.04 ± 0.66 | 71.39 ± 0.91 | 72.04 ± 1.19 |
| Single unsaturated fatty acid | 31.89 ± 1.39 | 31.41 ± 1.81 | 33.09 ± 1.66 | 33.59 ± 1.35 | 35.96 ± 3.81 |
| Poly unsaturated fatty acid | 40.31 ± 1.10 | 41.57 ± 1.19 | 37.95 ± 2.14 | 37.80 ± 1.24 | 36.08 ± 3.37 |
Each value represents mean ± SE
Asterisk marks (*) mean significant differences compared with control (PBS) group (p < 0.05)
In abdominal GB100 or GB200 fat tissue of 1-month treatment period, mono (single) unsaturated fatty acid composition was decreased whereas poly unsaturated fatty acid composition was increased with dose-dependent manner (each group vs CON, p < 0.05). In epididymidal fat tissue of GB100 or GB200 HFD rats of 1-month treatment period, the composition of docosahexaenoic acid in epdidymidal fat tissue showed dose-dependent decrease with significant difference (Gb200 vs CON, p < 0.05). In 1-month treatment groups, eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid composition were increased with statistical significance (GB100 vs CON, p < 0.05; STA vs CON, p < 0.05).
In abdominal fat of 2-month treated HFD rats, poly unsaturated fatty acid were increased, and monounsaturated fatty acid were dose-dependently decreased (each group vs CON, p < 0.05). Stearic acid composition in IS100 group was higher compared with control group (IS100 vs CON, p < 0.05).
In epididymidal fat of 2-month treated rats, arachidonic acid and docosahexaenoic acid composition in GB100 (GB100 vs CON, p < 0.05), and eicosanoic acid composition in IS100 showed significant differences compared with control (IS100 vs CON, p < 0.05).
Discussion
A high-fat diet (HFD) induces obesity and obesity related metabolic complications such as adipose inflammation, hepatic steatosis and hyperlipidemia [13]. Among various animal sources tested [14], cricket extract was found to be a potent functional food; the adipose tissue fat weight of Wistar rats treated with GB over a 2-month period was decreased, especially the abdominal fat and epididymidal fat. However, body weight was not significantly different in the GB treated and control groups.
Modulating inflammation in adipose tissue ameliorates obesity-associated metabolic complications [15]. GB extract slightly lowered blood pressure and creatinine phosphokinase or otherwise increased thrombin time, showing anticoagulant activity. Repair of protein oxidative damage caused by a high fat diet, carbonyl content and lipid oxidative damage (malondialdehyde, MDA) were decreased by GB treatment [16]. Hepatic mRNA expression of IL-10 was reported to be increased in obese C57BL6/J mice on high-fat diets [17] and overexpression of IL-10 prevented weight gain in animals on HFD [18].
A high-fat diet decreases energy expenditure and the expression of genes controlling lipid metabolism, mitochondrial function and skeletal system development in the adipose tissue, along with increased expression of extracellular matrix remodeling- and inflammation-related genes [19].
This study observed meaningful gene expression profiles. Compared to the control, the GB extract-treated rat group (at a dose of 100 and 200 mg/kg) had 190 up-regulated genes including Gpm6a (glycoprotein m6a) [20], Tmem14a (transmembrane protein 14A) [21] and Fasin (fatty acid synthase) [22] (Table 3) and 235 down-regulated genes including Cc121b (chemokine ligand 21b), Glycan1 (glycosylation dependent cell adhesion molecule [23], Serpinb1a (serine proteinase inhibitor) [24] and Tcrb (T-cell receptor beta chain) [16] (Table 4).
In accordance with the decreased weight of abdominal fat tissue, total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, and triglyceride in GB treated rats were lower than those of the control (PBS treated) group. In the sera of rats treated with GB for 1-month, free fatty acid levels were reduced in a dose-dependent manner. In addition, glucose, triglyceride and alkine phosphatase levels were also decreased in the 100 mg/kg GB extract-treated group. The composition of saturated fatty acid was decreased, while unsaturated fatty acid and poly unsaturated fatty acid were increased in the epididymal adipose tissue, suggesting that a diet rich in poly-unsaturated fatty acid decreases adipose tissue mass and suppresses the development of obesity in rats [3, 25].
Conclusions
GB demonstrated anti-lipidemic effects in Wistar high fat dieted rats by significantly reducing serum triglyceride and alkaline phosphatase levels. Consequently, GB may be a protective nutraceutical for atherosclerosis disorders, including circulatory disorders. The gene expression profile of high fat dieted Wistar rats treated with GB is a valuable prognostic marker that can be used to identify potential therapeutic targets for atherosclerosis.
Materials and methods
Materials
G. bimaculatus was reared in a cricket farm located in Jungsun, Kangwon-Do, South Korea. The cricket was freeze-dried at the Department of Agricultural Biology, National Academy of Agricultural Science, Korea.
Preparation of G. bimaculatus extract (GB)
Dried G. bimaculatus (1 kg) was homogenized and soaked then extracted three times with 70 % ethanol by ultrasonification for 30 min. The samples were filtered through Whatman filter paper and concentrated by evaporation and freeze-drying. The dried powder (ethanol extract, GB) was dissolved in saline prior to use in the test solution. Isaria sinclairii was also extracted with 70 % ethanol through sonication, evaporation and freeze-drying using the same method as for GB.
Animals
Han Tac Sam-WH (Wistar) rats (male), weighing 308.0 ± 11.0 g at 14-weeks of age, were obtained from Samtako Co. Ltd. (Osan, Korea) and divided into five groups of ten rats including the Wistar control group. All procedures were in accordance with the NIH Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. All experiments were approved by the Laboratory Animals’ Ethical Committee of the National Academy of Agricultural Science, RDA and followed national guidelines for the care and use of animals (individual housing). The rats were acclimated for four weeks under normal husbandry conditions (23 ± 2 °C, 55 ± 10 %, humidity and 12 h light/dark cycle) and fed a high (60 %) fat diet, D12492 (Research Diet Inc., USA) and water ad libitum. The rats were distributed into the following 5 groups (n = 10) with similar weights: I: control group, PBS treatment, II: treated with 100 mg/kg G. bimaculatus ethanol extract, III: treated with 200 mg/kg G. bimaculatus ethanol extract, IV: treated with 2 mg/kg Pravastatin (CJ Heathcare CO., Korea), V: 100 mg/kg Isaria sinclairii ethanol extract. Each group (5 sample groups) was maintained for a one month or two month- period (Scheme 1).
Scheme 1.
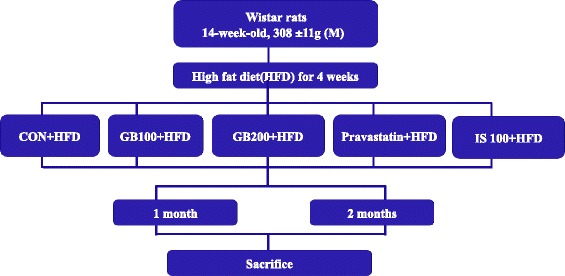
Animal experimental design
Organ weights
About five groups named CON, GB100, GB200, STA, IS100, divided 1 month- or 2 month- period subgroup (n = 5). The absolute and relative (organ-to-body weight ratios) weights of the following organs were measured: adrenal glands, kidneys, heart, liver, lung, spleen, stomach, pancreas, thymus and ovaries.
Blood sampling and blood, plasma, serum assay
On five groups named CON, GB100, GB200, STA, IS100, divided 1 month- or 2 month-period subgroup (n = 5), after 1 month of treatment, blood (~3 ml) was collected from the posterior vena cava under light CO2 inhalation and used for serum chemistry measurements. The parameters examined included total protein, total bilirubin, glucose, glutamic pyruvic transaminase (GPT), glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT), γ-glutamyl transferase (GGT), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), CK(creatinine phosphokinase), lactic dehydrogenase (LDH), total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), creatinine, triglyceride, uric acid, sodium, potassium and chloride. All parameters were evaluated using an autoanalyzer (Hitachi 7060 automatic clinical analyzer, Tokyo).
Liver homogenate preparation for oxidative damage detection
About five groups named CON, GB100, GB200, STA, IS100, divided 1 month- or 2 month- period subgroup (n = 5), liver tissues were homogenized on ice in a 10-fold volume lysis buffer PRO-PREP™ Protein extraction solution (iNtRON, Busan, Korea). The supernatant of the liver homogenate after centrifugation (800 g, 10 min) was assayed for carbonyl content or catalase activity.
Oxidative protein damage (carbonyl content and catalase) quantitation
On the supernatant of liver homogenate and blood of five groups named CON, GB100, GB200, STA, IS100, divided 1 month- or 2 month- period subgroup (n = 3), the carbonyl content was determined with an enzyme-linked immunoassay according to the manufacturer’s protocol for the OxiSelect™ protein carbonyl ELISA kit, Cell Biolabs, Inc. (Sandiego, USA). Catalase activity (CAT, U/mg protein) was measured according to the method based on CAT-mediated decomposition of H2O2. Potassium phosphate buffer (50 mM, pH 7.0, 0.9 ml) was added to 0.1 ml of the sample followed by H2O2 solution (1 ml, 30 mM). The decrease in the absorbance at 240 nm was measured for 90 s [26].
Oxidative lipid damage (malondialdehyde) quantitation
On five groups named CON, GB100, GB200, STA, IS100, divided 1 month- or 2 month- period subgroup (n = 3), to determine the oxidative lipid damage in GB treated rat hepatocytes, malondialdehyde (MDA) levels were measured with a lipid peroxidation assay using the color method involving thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) at 535 nm. The liver homogenate (0.5 ml) mentioned earlier as well as sodium dodecyl sulfate (7 % SDS, 1 ml) was incubated for 30 min at 37 °C before mixing with TBA (0.67 %, 2 ml, 1: 1 with acetic acid) and adding to tubes. The tubes were mixed, placed in boiling water (100 °C) for 50 min then mixed with butanol (5 ml). 1,1,3,3-tetraethoxypropane was used as a standard [27].
Cytokine IL-10 assay: R&D kit
On five groups named CON, GB100, GB200, STA, IS100, divided 1 month- or 2 month- period subgroup (n = 3), the IL-10 level in GB extract-treated rat serumwas measured using commercial ELISA kits (Quantikine, R&D Systems, Inc., Minneapolis, MN, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
DNA microarray procedure
After histopathology analysis, microarray hybridization was performed on liver samples (Control, GB 100 and GB200). The total RNA was isolated from the liver using a Qiagen RNeasy Midi Kit (Qiagen, Valencia, USA). A regular microarray was carried out according to the manufacturer’s instructions for the FairPlay™ microarray labeling kit (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA). Briefly, 20 μg total RNA from the liver was reverse-transcribed into single stranded cDNA. The cDNA was purified with ethanol precipitation and resuspended in 5 μl of 2x coupling buffer, then coupled with 5 μl of Cy3 or Cy5 dye for 1 h in the dark. The labeled control liver cDNA and the treated liver cDNA were combined and purified. The labeled cDNA was mixed with 1.5 μl of 10 μg/μl salmon DNA, 1.5 μl of 8 μg/μl poly d(A), 1.5 μl of 4 μg/μl yeast tRNA, 4.5 μl of 20x SSC and 0.75 μl of 10 % SDS, heated at 99 °C for 2 min, and incubated at 45 °C for 15 min. The labeled DNA was loaded onto a microarray chip. A hybridization chamber was assembled with the microarray chip and submerged in a water bath overnight at 60 °C. The microarray chip was washed in wash buffer I (2x SSC, 0.1 % SDS) for 15 min, then in wash buffer II (1x SSC) for 5 min and in wash buffer III (0.2x SSC) for 15 min. The slide was dried by centrifuging at 500 g for 15 min and scanned with a BMS Array Scanner, applied precision Array WoRx eBiochip Reader (BioRad, Dallas, USA) using the Cy3 and Cy5 channels [28].
Analysis of fatty acid composition in rat adipose tissue
On five groups named CON, GB100, GB200, STA, IS100, divided 1 month- or 2 month- period subgroup (n = 4), for epididymidal and abdominal fat analysis, the concentrations of free fatty acids and fatty acid composition were analyzed for 29 fatty acids in adipose tissue using gas chromatography-mass spectroscopy (GC-MS). Each cut adipose or epididymidal tissue (0.1 g) was collected and extracted overnight bwith a chloroform: methanol (2:1) mixture. The filtered solution was removed under nitrogen gas. The lipids were then saponified by alkaline hydrolysis of phospholipids at 100 °C with 0.5 N methanolic sodium hydroxide and methylated at 100 °C with 14 % BF3 for 15 min. The top layer was transferred to petroleum ether and analyzed by GC/MS (Aglient 6890GC, Aglient 5973 N mass detector, EI mode) with a HP-5 capillary column (Aglient Technolgies, Palto alto, Ca, USA). The inlet temperature was 250 °C and the MS transfer line was kept constant at 230 °C. The oven temperature was held at 180 °C for 20 min, then programmed at 10 °C/min to 230 °C and held for 10 min. Quantification was achieved using a mixed 37 fatty acid standard: Sigma L9405, 10 ρg/mL (Sigma-Aldrich Inc.). Linoleic acid (C18:2n6) was used as an internal standard.
Statistical analysis
The means and standard error of all parameters studied were determined for each group using the ANOVA test. A Student’s t-test was carried out to determine significant differences between control and treated groups. A p value <0.05 was considered significant.
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the Rural Development Administration National Research project, PJ009827.
Abbreviations
- ALP
Alkaline phosphatase
- ALT(GPT)
Glutamate pyruvate transaminase
- AST(GOT)
Glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase
- BUN
Blood urea nitrogen
- Ca
Calcium
- CK
Creatinine phosphokinase
- Cl
Chloride
- CRP
C-reactive protein
- FFA
Free fatty acid
- GB
Gryllus bimaculatus ethanol extract
- GB100
Gryllus bimaculatus ethanol extract 100 mg/kg
- GB200
Gryllus bimaculatus ethanol extract 200 mg/kg
- GGT
γ-glutamyl transferase
- H. Chol
High cholesterol
- HFD
High-fat diet
- Hct
Hematocrit
- Hgb
Hemoglobin
- l.Chol
Low cholesterol
- IP
Inorganic phosphorus
- IS100
I. sinclairii ethanol extract 100 mg/kg
- LDH
Lactate dehydrogenase
- MCH
Mean corpuscular hemoglobin
- MCHC
Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration
- MCV
Mean corpuscular volume
- K
Potassium
- Na
Sodium
- T. Chol
Total cholesterol
- TG
Triglyceride
- PLT
Partial thromboplastin time
- STA
Provastastin
- PT
Prothrombin time
- RBC
Red blood cell
- T. Bil
Total bilirubin
- WBC
White blood cell
Footnotes
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
MY Ahn performed most of the experiments, prepared the manuscript: conceived of the study, participated in its design and coordination, collected and analyzed data, and drafted the manuscript. MJ Kim carried out the animal studies, participated in the fatty acid analysis and oxidative relating enzyme assay. RH Kwon carried out the MDA and catalase assays. JS Hwang participated in the genetic sequence alignment. KK Park participated in DNA microarray. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
References
- 1.Lee CY. The effect of high-fat diet-induced pathophysiological changes in the gut on obesity: What should be the ideal treatment? Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2013;4:e39. doi: 10.1038/ctg.2013.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Oh TS, Yun JW. DNA microarray analysis reveals differential gene expression in the soleus muscle between male and female rats exposed to a high fat diet. Mol Biol Rep. 2012;39:6569–80. doi: 10.1007/s11033-012-1486-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Yunoki K, Sasaki G, Tokuji Y, Kinoshita M, Naito A, Aida K, et al. Effect of dietary wine pomace extract and oleanolic acid on plasma lipids in rats fed high-fat diet and its DNA microarray analysis. J Agric Food Chem. 2008;56:12052–8. doi: 10.1021/jf8026217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Dudley KJ, Sloboda DM, Connor KL, Beltrand J, Vickers MH. Offspring of mothers fed a high fat diet display hepatic cell cycle inhibition and associated changes in gene expression and DNA methylation. PLoS One. 2011;6:e21662. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ahn MY, Bae HJ, Kim IS, You EJ, Kwack SJ, Kim HS, et al. Genotoxic evaluation of the biocomponents of the cricket, Gryllus bimaculatus, using three mutagenicity tests. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2005;68:2111–8. doi: 10.1080/15287390500182537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ahn MY, Ryu KS, Park BY, Kim DW, Kim I, Kim SH. Effects on cricket supplements on the chicken meats and its eggs. Korean J Poult Sci. 2000;27:197–202. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ahn MY, Lee YW, Ryu KS, Lee HS, Kim IK, Kim JW, et al. Effect of water and methanol extracts of cricket (Gryllus bimaculatus) on alcohol metabolism. Korean J Pharmacogn. 2004;35:175–8. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ahn MY, Lee YW, Ryu KS, Lee HS, Kim IK, Kim JW, et al. Protective effects of water/methanol extracts of cricket on the acute hepatic damages in the ICR-mice induced by administration of CCl4. Korean J Food Sci Technol. 2002;34:684–7. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ahn MY, Jee SD, Lee BM. Antiobesity effects of Isaria sinclairii by repeated oral treatment in obese Zucker rats over a 4-month period. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2007;70:1395–401. doi: 10.1080/15287390701428556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ahn MY, Jee SD, Lee BM, Yeon JH. Park, KK, Hwang JS, Yun EY: Antidiabetic effects and gene expression profiling in obese mice treated with Isaria sinclairii over a 6-month period. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2010;73:1511–20. doi: 10.1080/15287394.2010.511575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ahn MY, Jung YS, Jee SD, Kim CS, Lee SH, Moon CH, et al. Anti-hypertensive effect of the Dongchunghacho, Isaria sinclairii, in the spontaneously hypertensive rats. Arch Pharm Res. 2007;30:493–501. doi: 10.1007/BF02980225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Nozue T, Yamamoto S, Tohyama S, Fukui K, Umezawa S, Onishi Y, et al. Comparison of effects of serum n-3 to n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid ratios on coronary atherosclerosis in patients treated with pitavastatin or pravastatin undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. Am J Cardiol. 2013;111:1570–5. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2013.01.327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Gao M, Ma Y, Liu D. High-fat diet-induced adiposity, adipose inflammation, hepatic steatosis and hyperinsulinemia in outbred CD-1 Mice. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0119784. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Attia YA, Al-Harthi MA, Shiboob MM. Evaluation of quality and nutrient contents of table eggs from different sources in the retail market. Ital J Anim Sci. 2014;13:369. doi: 10.4081/ijas.2014.3294. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Jung UJ, Choi MS. Obesity and its metabolic complications: the role of adipokines and the relationship between obesity, inflammation, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15:6184–223. doi: 10.3390/ijms15046184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Khan IM, Dai Perrard XY, Perrard JL, Mansoori A, Smith CW, Wu H, et al. Attenuated adipose tissue and skeletal muscle inflammation in obese mice with combined CD4+ and CD8+ T cell deficiency. Atherosclerosis. 2014;233:419–28. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2014.01.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Farrell GC, Mridha AR, Yeh MM, Arsov T, Van Rooyen DM, Brooling J, et al. Strain dependence of diet-induced NASH and liver fibrosis in obese mice is linked to diabetes and inflammatory phenotype. Liver Int. 2014;34:1084–93. doi: 10.1111/liv.12335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Gao M, Zhang C, Ma Y, Bu L, Yan L, Liu D. Hydrodynamic delivery of mIL10 gene protects mice from high-fat diet-induced obesity and glucose intolerance. Mol Ther. 2013;21:1852–61. doi: 10.1038/mt.2013.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Choi MS, Kim YJ, Kwon EY, Ryoo JY, Kim SR, Jung UJ. High-fat diet decreases energy expenditure and expression of genes controlling lipid metabolism, mitochondrial function and skeletal system development in the adipose tissue, along with increased expression of extracellular matrix remodeling- and inflammation-related genes. Br J Nutr. 2015;113:867–77. doi: 10.1017/S0007114515000100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Horowitz S, Horowitz A, Nilsen TW, Munns TW, Rottman FM. Mapping of N6-methyladenosine residues in bovine prolactin mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984;81:5667–71. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Woo IS, Jin H, Kang ES, Kim HJ, Lee JH, Chang KC, et al. TMEM14A inhibits N-(4-hydroxyphenyl) retinamide-induced apoptosis through the stabilization of mitochondrial membrane potential. Cancer Lett. 2011;28(309):190–8. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2011.05.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Sider KL, Zhu C, Kwong AV, Mirzaei Z, de Langé CF, Simmons CA. Evaluation of a porcine model of early aortic valve sclerosis. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2014;23:289–97. doi: 10.1016/j.carpath.2014.05.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Frank J, Kaulfürst-Soboll H, Rips S, Koiwa H, von Schaewen A. Comparative analyses of Arabidopsis complex glycan1 mutants and genetic interaction with staurosporin and temperature sensitive3a. Plant Physiol. 2008;148:1354–67. doi: 10.1104/pp.108.127027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Madsen L, Petersen RK, Kristiansen K. Regulation of adipocyte differentiation and function by polyunsaturated fatty acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005;1740(2):266–86. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2005.03.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Slawik M, Vidal-Puig AJ. Lipotoxicity, overnutrition and energy metabolism in aging. Ageing Res Rev. 2006;5:144–64. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2006.03.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kang KS, Kim ID, Kwon RH, Lee JY, Kang JS, Ha BJ. The effects of fucoidan extracts on CCl4-induced liver injury. Arch Pharm Res. 2008;31:622–7. doi: 10.1007/s12272-001-1203-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kim ID, Ha BJ. The effects of Paeoniflorin on LPS-induced liver inflammatory reactions. Arch Pharm Res. 2010;33:959–66. doi: 10.1007/s12272-010-0620-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Song J, Liu H, Ressom HW, Tiwari S, Ecelbarger CM. Chronic Rosigiltazone therapy normalizes expression of ACE1, SCD1 and other genes in the kidney of obese Zucker rats as determined by microarray by microarray analysis. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2008;116:315–25. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1042429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


