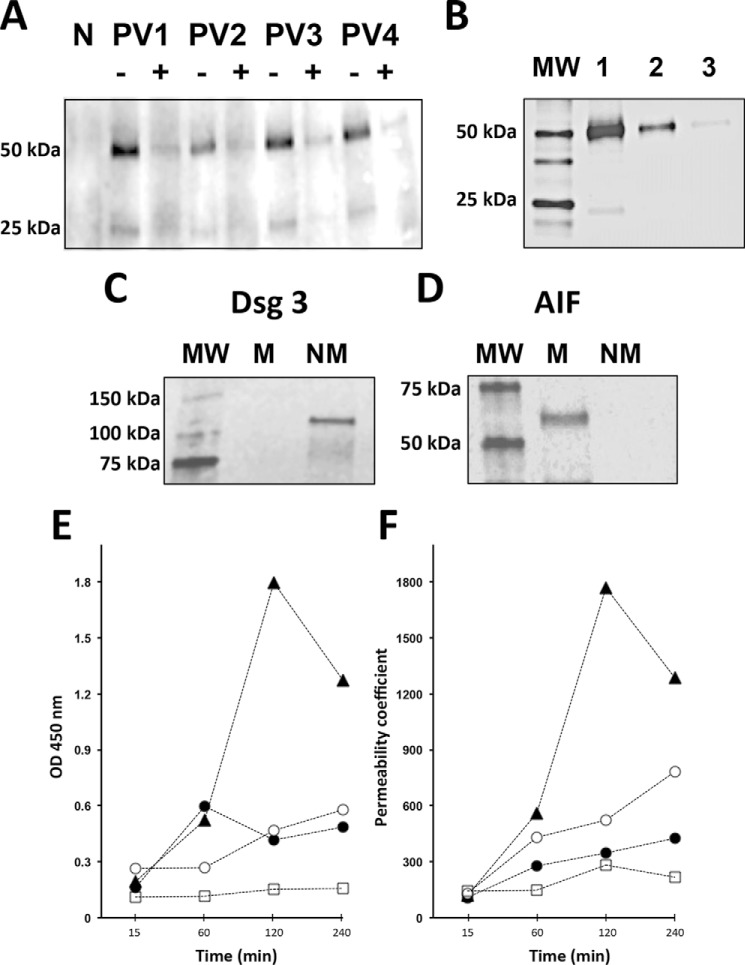
FIGURE 1.
Indispensable role of FcRn in the AMA-mediated damage of KCs. A, WB study of the ability of PVIgGs to reach mitochondrial targets in KCs. The monolayers of KCs grown to ∼80% confluence at 37 °C and 5% CO2 were preincubated for 15 min with 2 μg/ml mouse monoclonal antibody against the extracellular domain of human FcRn or an equal amount of nonimmune mouse IgG (control) and then were exposed for 16 h to 1 mg/ml PVIgG from four patients or NIgG. The mitochondrial protein fraction of exposed cells was isolated as detailed under “Experimental Procedures,” separated by SDS-PAGE, and probed with HRP-conjugated anti-human IgG antibody that visualized PVIgG's heavy and light chains. Pretreatment of keratinocyte monolayer with anti-FcRn antibody (+), but not with control mouse IgG (−), abolished detection of PVIgGs in the subcellular mitochondrial fraction. N = NIgG. B, dose-dependent inhibition of AMA entry of KCs by anti-FcRn antibody. Following the protocol described in the legend to A, the monolayers of KCs were exposed to 1 mg/ml pooled PVIgGs (PV1 + PV3 + PV4) in the presence of 0 (lane 1), 1 (lane 2), or 2 (lane 3) μg/ml anti-FcRn antibody, after which each mitochondrial fraction was isolated and stained for human IgG. The molecular mass (lane MW) markers are shown on the left lane. C and D, control WB experiments showing purity of the nonmitochondrial (NM) and mitochondrial (M) fractions of KCs. The NM fraction, which was composed of the cell membrane and cytosol proteins, and the M fraction were isolated as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The staining for the cell membrane protein Dsg3 is present in the nonmitochondrial but not in the mitochondrial fraction (C), whereas that for the mitochondrial protein apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF) in the mitochondrial but not the nonmitochondrial fraction (D). E, time course study of CytC release in human KCs treated with AMA with or without the anti-FcRn antibody or non-AMA. To obtain AMA, the IgGs isolated from sera four PV patients were pooled and preabsorbed with a mixture of both the cytosolic and the cell membrane protein fractions of KCs, whereas non-AMA were obtained by preabsorption of PVIgGs with the mitochondrial protein fraction (both protein fractions were tested for purity in C and D). Both the AMA and non-AMA were used in the CytC release as detailed under “Experimental Procedures.” KCs were incubated at 37 °C and 5% CO2 for the indicated periods of time in culture medium containing 1.6 mm Ca2+ in the presence of test PVIgGs. Before exposure to AMA, some monolayers were preincubated for 15 min with 2 μg/ml anti-FcRn antibody. The data were obtained in three independent experiments. ▴, AMA; ●, AMA + anti-FcRn antibody; ○, non-AMA; □, NIgG. F, time course study of permeability of keratinocyte monolayers treated with AMA with or without anti-FcRn antibody or non-AMA. KCs grown to confluence on the membrane-bottomed tissue culture insets were exposed to test antibodies, and permeability of the monolayer was determined by measuring the amount of the radioactive tracer moving between cells across the monolayer into the lower chamber as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The data were obtained in three independent experiments. The designations are the same as in E.