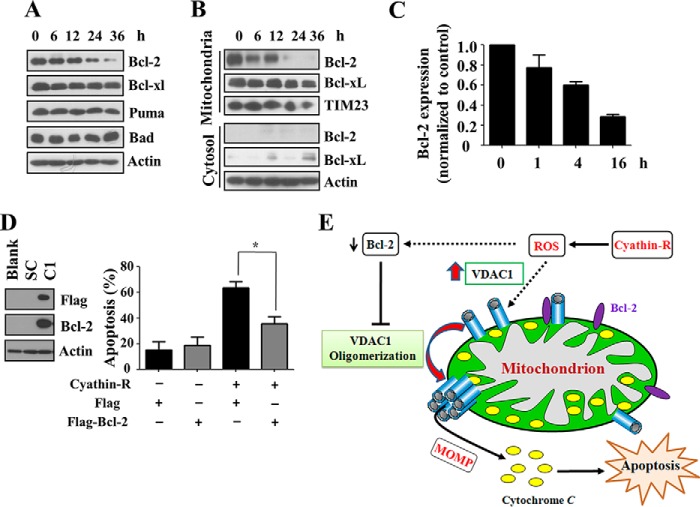
FIGURE 10.
Bcl-2 regulates cyathin-R-induced VDAC1 oligomerization and apoptosis. A–C, Bax−/−/Bak−/− MEFs were treated with 3 μm cyathin-R for the indicated times, and the indicated proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting. A, cells were fractionated into mitochondrial and cytosol fractions, and Bcl-2 was analyzed by immunoblotting, with actin and Tim23 serving as input controls (B). Bcl-2 mRNA levels were monitored by quantitative real-time PCR (C). Means ± S.E. (error bars) (n = 3) are presented. D, a FLAG-tagged Bcl-2 vector was transfected into Bax−/− HCT116 cells, and stable Bcl-2-overexpressing cells were acquired using puromycin. Stable Bcl-2-overexpressing Bax−/− HCT116 and control cells were treated with cyathin-R (5 μm, 24 h) and analyzed for apoptosis. Means ± S.E. (n = 3) are presented. E, proposed model of cyathin-R-induced apoptosis. Cyathin-R, through a triggering of oxidative stress, causes augmentation of VDAC1 levels that in turn shifts the equilibrium toward VDAC1 oligomerization, allowing cytochrome c release, which leads to apoptosis. The decrease of Bcl-2 facilitates oligomerization of VDAC1, leading to apoptosis. *, p < 0.05.