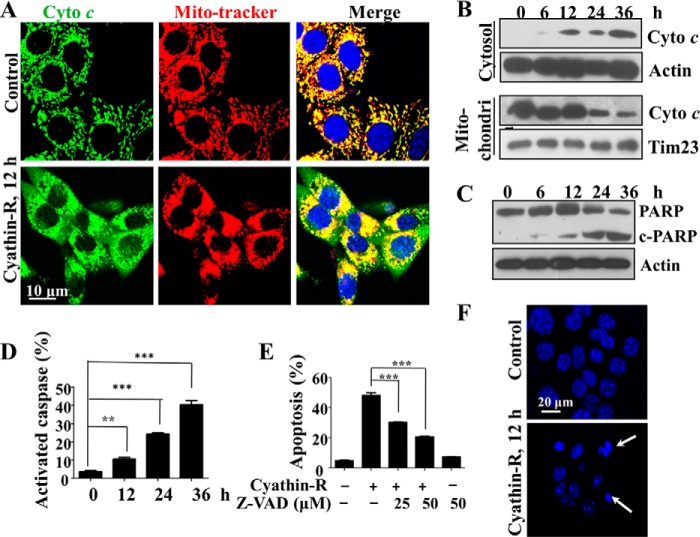
FIGURE 2.
Cyathin-R induces apoptosis in Bax−/−/Bak−/− MEFs. A, cytochrome c release from mitochondria; Bax−/−/Bak−/− MEFs treated with 3 μm cyathin-R for the indicated times, as analyzed by immunohistochemistry using anti-cytochrome c antibodies, with nuclei stained with DAPI and mitochondria with MitoTracker. Cells were visualized by confocal microscopy. The enlarged images on the right are from the boxed areas. Scale bar, 20 μm. B, cytochrome c (Cyto c) release as assayed by immunoblotting of cytosolic and mitochondrial fractions. C, poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) cleavage; Bax−/−/Bak−/− cells were treated with 3 μm cyathin-R for the indicated times. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase cleavage was analyzed by immunoblotting. D, caspase activation; Bax−/−/Bak−/− MEFs were treated as described in the legend to Fig. 1G and then stained with a CaspACE-FITC-conjugated caspase marker. Means ± S.E. (error bars) (n = 3) are shown. E, apoptosis inhibition with casapse inhibitor; Bax−/−/Bak−/− MEFs were pretreated with Z-VAD-fmk casapse inhibitor (1 h) and then incubated with cyathin-R (5 μm, 24 h). Cell death was analyzed by annexin-V/PI staining and flow cytometry. Means ± S.E. (n = 3) are presented. F, cell nuclear fragmentation; Bax−/−/Bak−/− cells were treated with 3 μm cyathin-R, stained with Hoechst 33342, and imaged by confocal microscopy. Scale bar, 20 μm. **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.