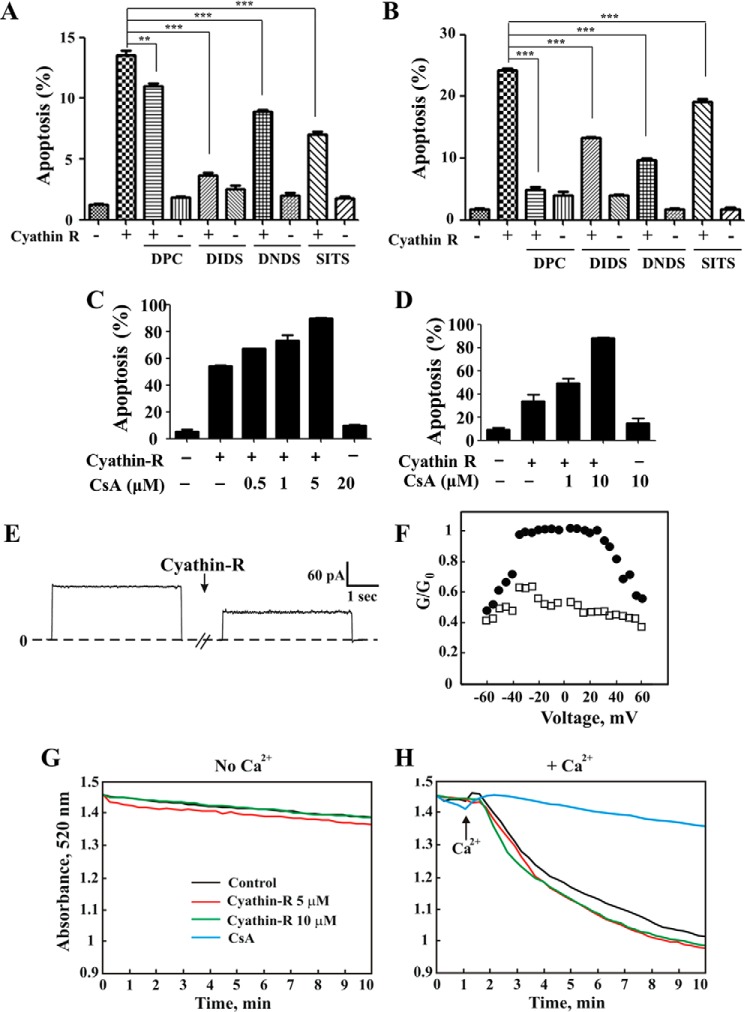
FIGURE 4.
VDAC1-interacting molecules but not cyclosporine A inhibit cyathin-R-induced apoptosis. Where indicated, apoptosis was analyzed by annexin-V/PI staining and flow cytometry. A and B, Bax−/−/Bak−/− MEFs (A) and Bax−/− HCT116 colon cancer cells (B) were pretreated with 0.5 mm DpC, DIDS, DNDS, or SITS (1 h) at the indicated concentrations, incubated with cyathin-R (5 μm, 24 h), and analyzed for apoptosis. Means ± S.E. (error bars) (n = 3) are presented. C and D, Bax−/−/Bak−/− MEFs (C) or Bax−/− HCT116 colon cancer cells (D) were pretreated with cyclosporin A (CsA) at the indicated concentrations, incubated with 5 μm cyathin-R, and analyzed for apoptosis. Means ± S.E. (n = 3) are presented. E, cyathin-R reduces VDAC1 channel conductance. VDAC1 was reconstituted into a planar lipid bilayer as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Currents through VDAC1 in response to a voltage step from 0 to 10 mV were recorded before and 30 min after the addition of cyathin-R (5 μm). F, VDAC1 conductance as a function of voltage, from 60 to −60 mV, was recorded before (●) and after (○) the addition of cyathin-R. The average steady-state conductance at a given voltage (G) was normalized to the maximal conductance at 10 mV (G0). G and H, effect of cyathin-R on the mPTP. PTP opening was assayed as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The effect of cyathin-R (5 μm) on mPTP opening in the absence (G) or the presence of Ca2+ (50 μm) (H) was monitored by following changes in absorbance at 520 nm, monitored every 15–20 s with an Ultraspec 2100 spectrophotometer. **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.