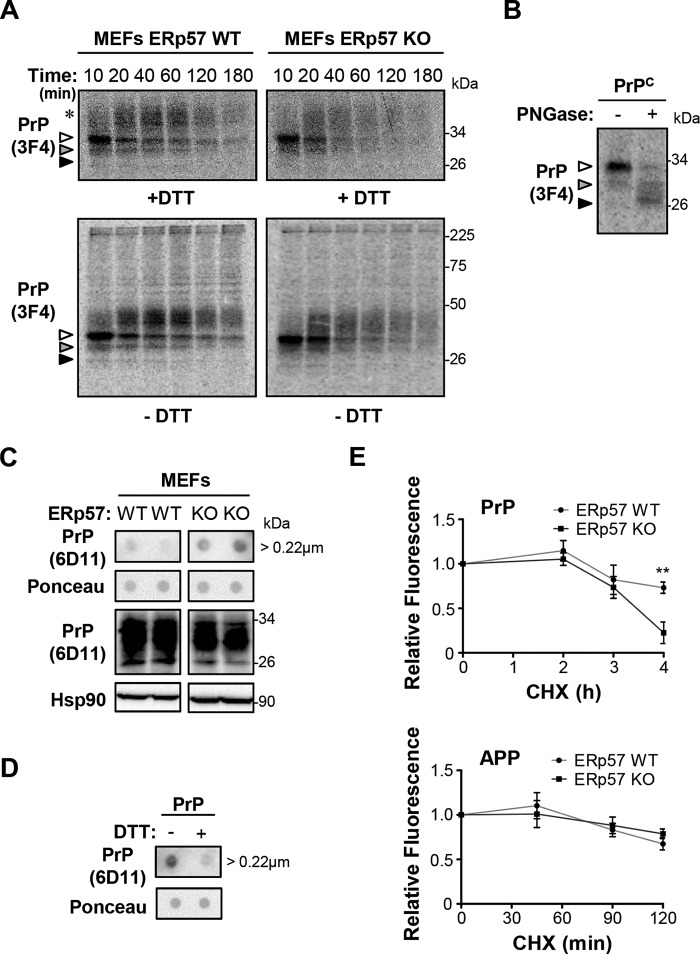
FIGURE 4.
Effects of ERp57 on PrP maturation. A, ERp57-deficient (ERp57KO) and wild-type control (ERp57WT) MEFs were transfected with a construct for PrPC-3F4. After 16 h, a radioactive pulse was conducted with 0.10 mCi of 35S-Promix per plate. The chase of PrP protein was performed from 10 to 180 min. Then cells were lysed, and PrP was purified by immunoprecipitation using anti-PrP (3F4) antibody. Samples were analyzed in 12% SDS-polyacrylamide gels under thiol-reducing (+DTT, upper panel) and nonreducing (−DTT, lower panel) conditions and revealed by autoradiography. White, gray, and black arrowheads indicate di-, mono-, and nonglycosylated forms of PrP, respectively. The asterisk indicates higher molecular weight forms of PrP containing more complex glycosylations. B, deglycosylation analysis of PrPC in MEFs after treatment of protein extracts with PNGase F. The different glycosylation states of PrP are identified as in A. C, filter-tap analysis of aggregates of endogenous PrPC in ERp57-deficient and control MEFs under basal conditions. Dot-blots on PVDF membrane followed by Ponceau S staining or Western blot analysis of Hsp90 and PrP were performed as loading controls. Bands were cropped from their original position for the clarity of presentation. All samples were run in the same electrophoresis and detected in the same Western blot. D, thiol reduction assay using dithiothreitol (DTT) was performed to determine the dependence of PrPC aggregates on disulfide cross-links using filter-trap analysis. Dot-blot on PVDF membrane followed by Ponceau S staining was used as the loading control. E, ERp57-deficient and wild-type MEFs were transfected with PrPC-GFP or APP-GFP constructs. After 48 h, cells were treated with 50 μg/ml cycloheximide (CHX) for indicated time points, and fluorescence intensity was measured by flow cytometry. The initial fluorescence was normalized to 1 unit for control cells to monitor relative protein decay over time. Data represent the average and standard error of three independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed using two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test. Mean ± S.E. shown; **, p ≤ 0.01.