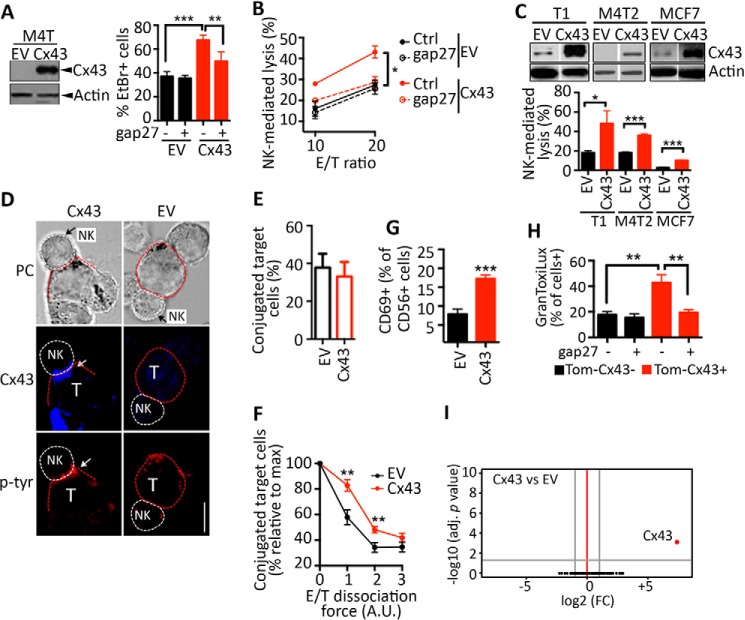
FIGURE 2.
Ectopic overexpression of Cx43 in melanoma cells improves their susceptibility to NK cell-mediated lysis. A, left panel, M4T melanoma cells were transfected with EV or a vector encoding Cx43. The overexpression of Cx43 was determined by Western blot analysis. Right panel, the uptake of EtBr by M4T-EV or M4T-Cx43 cells was determined in the presence of a control (−) or the Cx43 inhibitor peptide gap27 (+). The percentage of EtBr+ cells is reported. B, the percentage of NK cell-mediated lysis of M4T-EV or M4T-Cx43 cells. Cells were cocultured with NK92 cells at a 10/1 (10) or 20/1 (20) E/T ratio in the presence of a control (Ctrl) or the Cx43 inhibitor peptide gap27. C, top panel, the melanoma cell lines T1 and M4T2 and the breast cancer cell line MCF7 were stably transfected with EV or a vector encoding Cx43. Cx43 and β-actin protein levels were determined by Western blot analysis. Bottom panel, NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity was determined at a 10/1 E/T ratio. D, M4T-EV or M4T-Cx43 cells were cocultured with NK92 cells. NK cell/target (T) conjugates were analyzed by phase-contrast (PC) microscopy. Cx43 and Tyr(P) accumulation at the immune synapse is indicated by white arrows. Scale bar = 5 μm. E and F, M4T-EV or M4T-Cx43 cells were loaded with Dil-CM and cocultured for 10 min with TFL4-loaded NK92 cells at a 3/1 E/T ratio. E, the percentages of target cells conjugated with NK cells were assessed by flow cytometry. F, cell conjugates were subjected to increasing dissociation forces (vortex setting: 1, low; 2, medium; 3, high velocity) for 30 s. The percentages of target cells conjugated with NK cells are reported as the percentage relative to the maximum (no vortex). A.U., arbitrary unit. G, NK92 cells were cocultured for 4 h with M4T-EV or M4T-Cx43 cells. The expression of CD69 on the surface of NK cells was determined by flow cytometry. H, M4T cells were transfected with Tomato fused to Cx43 (Tom-Cx43). Cells were labeled with TFL4 and cocultured with NK92 cells for 1 h at a 3/1 E/T ratio in the presence of a permeable fluorogenic substrate for GzmB (GranToxiLux). GzmB activity was evaluated on TFL4+Tom-Cx43− or TFL4+Tom-Cx43+ M4T cells by flow cytometry. Shown is the percentage of GranToxiLux-positive target cells cocultured with NK92 cells in the presence of control (−) or gap27 peptides (+). I, volcano plots of gene expression (log2 -fold change, FC) and adjusted (adj) p values for M4T cells stably transfected with Cx43 versus the control EV. Data were obtained by analyzing the gene expression profiles of four independent clones per condition. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.