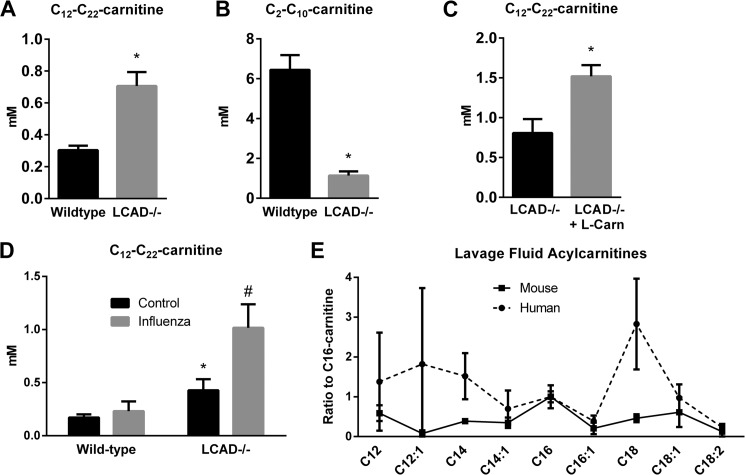
FIGURE 2.
LCAD−/− lungs accumulate long-chain acylcarnitines. Wild-type and LCAD−/− mice (n = 5) were fasted overnight and then lavaged with 50% acetonitrile/0.3% formic acid. The BALF was analyzed for 66 acylcarnitine species using mass spectrometry. LCAD−/− mice have (A) significantly increased total long-chain acylcarnitine species, and (B) significantly decreased short-chain species. C, carnitine supplementation increases long-chain acylcarnitine secretion even further in LCAD−/− mice, indicating that free carnitine is rate-limiting in the lung. D, stressing the lung with infection (influenza) also stimulates acylcarnitine secretion. E, five human lungs and three mice were lavaged with saline and acylcarnitine profiling performed. *, p < 0.01, LCAD−/− versus control.