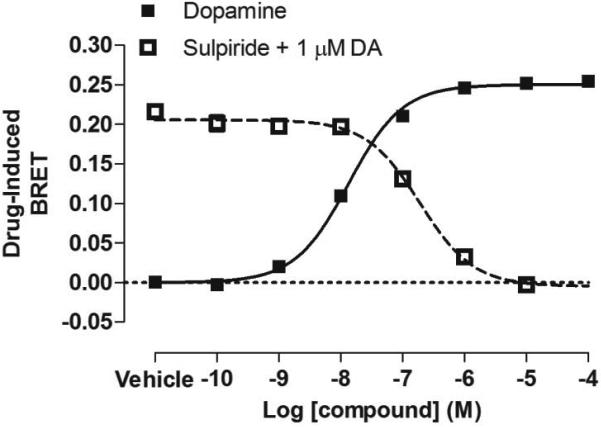
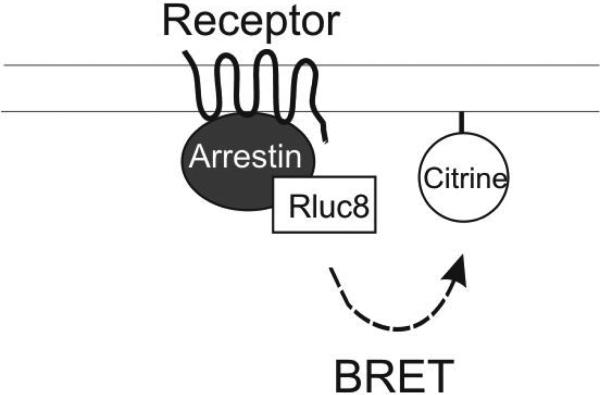
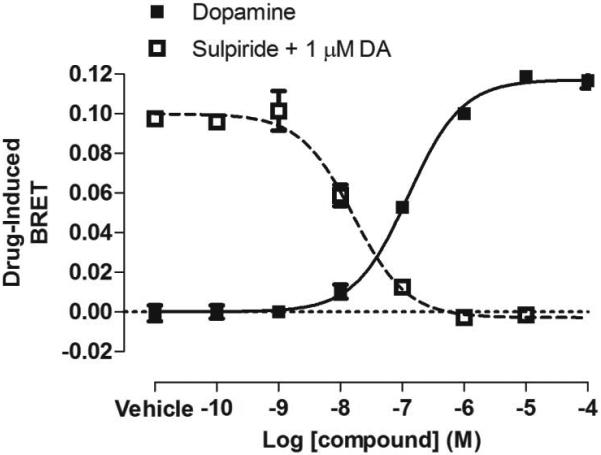
Figure 1. BRET-based arrestin-GPCR interaction assays.
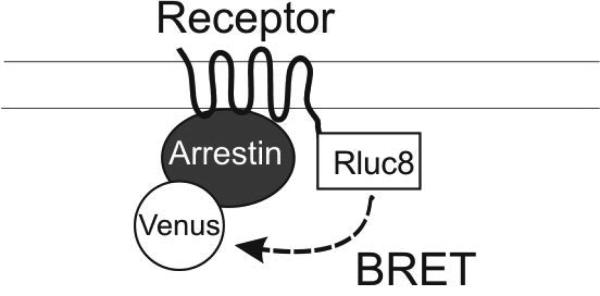
A. Schematic of the receptor-arrestin BRET assay, wherein a receptor is fused to the donor Rluc8 at its C-terminus and arrestin is fused to the acceptor Venus. Receptor activation results in an increase in BRET between the donor and acceptor molecules. B. Representative dose-response curves for the receptor-arrestin BRET assay shown in panel A. D2R-Rluc8 was activated dose dependently with dopamine (agonist mode). Additionally, activation of D2R with 1 μM dopamine was inhibited dose-dependently with the antagonist sulpiride (antagonist mode). C. Schematic of arrestin translocation BRET assay. Arrestin is fused to Rluc8 and an unrelated plasma membrane marker is fused to the acceptor citrine. Activation of the unmodified receptor results in translocation of arrestin to the plasma membrane and an increase in BRET between the donor and acceptor molecules. D. Representative dose-response curves for the arrestin translocation BRET assay shown in panel C. The experiments were performed, as described for panel B.