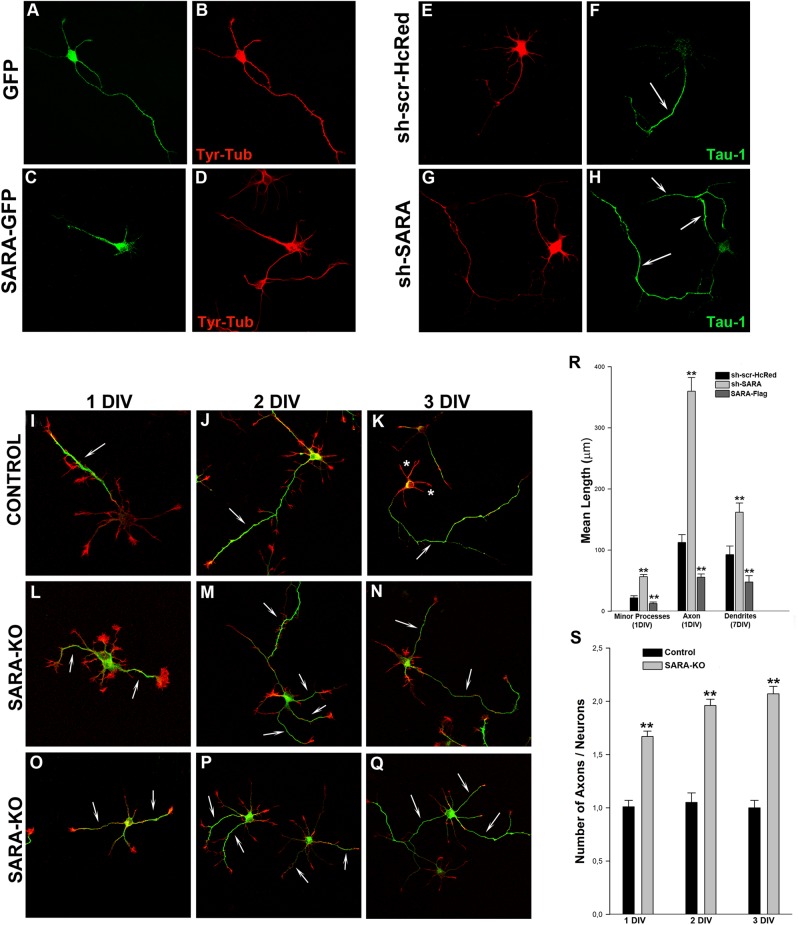
Fig 4. SARA suppression enhances axon elongation and induces formation of supernumerary axons.
(Upper panel, left) Morphology of 1 DIV neurons transfected with GFP (A) or SARA-GFP (C), double stained with a mAb against Tyr-Tubulin (B and D). Note that neurons with overexpressed SARA have their neuritic development arrested or delayed. (Upper panel, right) Images showing examples of neurons treated with control sh-scr-HcRed (control; E-F) or sh-SARA (G-H). Cultures were transfected with the corresponding plasmids (1–2 μg DNA each) 24 h after plating and counterstained with a mAb against the axonal marker Tau-1 (green, F-H). Note that SARA suppression increases axonal length and produces the formation of supernumerary axons (arrows in H), contrasting with the single axon in control neurons (arrow in F). Quantification of neurite length in knockdown SARA neurons reveals a significant increase in minor processes, axons and dendrites (**p<0.001; R), respect to the control or SARA overexpressed neurons. For dendrite measurement, neurons were transfected with the same constructs but at 7 DIV and counterstained with a mAb against MAP2, a marker of neuronal dendrites. (Bottom panel) Hippocampal pyramidal neurons from control mice (I-K) or SARA-KO mice (L-Q) fixed at 1, 2 or 3 DIV and stained with a mAb against Tau-1 (green) and Rhodamine-Phalloidin (red). Note that the most of SARA-KO neurons show two or more axons (arrows). Confocal images were from independent experiments, litter mice, and different pregnant females. Bar graph shows average number of Tau-1-positive axons / 50 neurons analyzed (**p<0.001; S).