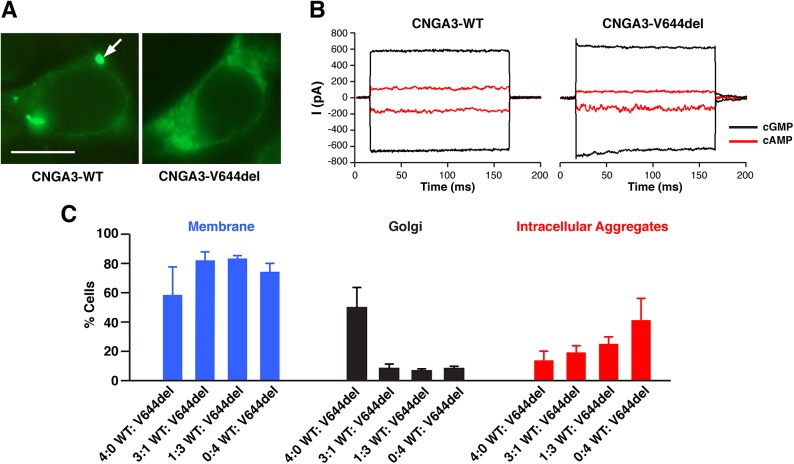
Fig 5. Complex cellular phenotype of V644del mutant channel.
(A) Cellular localization of YFP-tagged wild-type canine CNGA3 and CNGA3-V644del mutant in HEK tsA201 cells. Cells transfected with the wild-type construct showed specific fluorescence pattern of expression limited to the plasma membrane and Golgi-like organelles (arrow); an evident increase in intracellular aggregates was observed in cells transfected with V644del mutant construct consistent with abnormal trafficking and potential ER retention. Scale bar: 10μm. (B) cGMP- and cAMP-activated currents recorded from CNGA3-WT and a responsive patch expressing V644del mutant channels. Approximately 40% of V644del mutant patches had no cGMP-activated currents, in contrast to 100% responsive patches from the CNGA3-WT-transfected cells. This partial loss of channel activity might reflect incomplete subunit assembly associated with disruption of the coiled-coil structure as depicted in the simulation studies. The responsive patches showed cyclic nucleotide-activated currents with similar characteristics to WT channels. (C) Histograms of subcellular localization patterns monitored in HEK tsA201 cells co-transfected with V644del and CNGA3-WT cDNA constructs. Cells were transfected with either CNGA3-WT or CNGA3-V644del or both constructs at the indicated ratios. Each cell count represents >300 cells from at least 2 transfections (mean% ± SD).