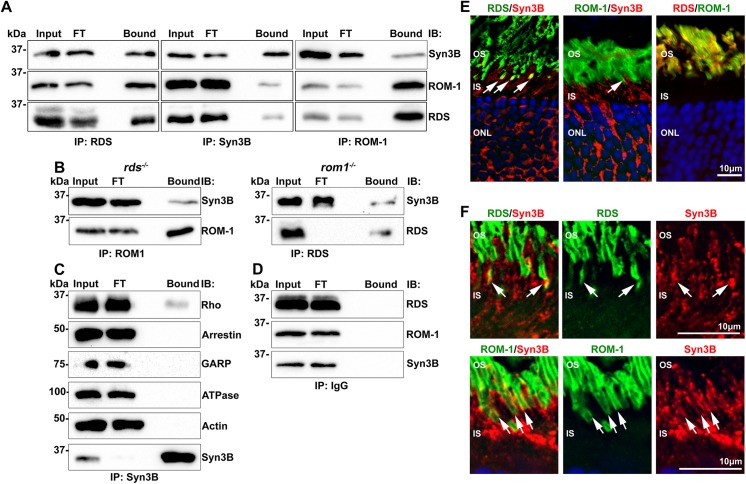
Fig 3. RDS and ROM-1 interact in vivo with Syn3B.
A. Retinal extract from WT mice underwent reciprocal co-IP for RDS (RDS-CT), ROM-1 (mAB 2H5), and Syn3B (Syn3B-478 [22]) antibodies, and WB analysis was used to detect binding partners (RDS, mAB 2B7, ROM-1, mAB 2H5, Syn3B, mAB 12E5). B. IPs were performed using ROM-1 mAB 2H5 and RDS-CT antibodies from retinal extract from rds -/- and rom1 -/- mice, respectively. Blots were probed for RDS (RDS-CT), ROM-1 (mAb 2H5) and Syn3B (mAb 12E5) antibodies. C. IP with anti-Syn3B (mAB 12E5) was performed on WT retinal extract and WBs were probed with antibodies against rhodopsin (Rho), arrestin 1, GARP, Na+/K+-ATPase (ATPase) and actin. None of the tested proteins except rhodopsin was detected after the pull down with Syn3B. D To ensure specificity of interactions, WT retinal extracts underwent IP with protein A beads and rabbit IgG. Resulting blots were probed for RDS (mAB 2E7), ROM-1 (mAB 2H5), and Syn3B (mAB 12E5). FT: flow through. E. Distribution of RDS (RDS-CT, green), ROM-1 (ROM1-CT, green middle, mAB 2H5, red right), and Syn3B (mAB 12E5, red) in the outer retina was assessed by IF, arrows show regions of co-localization. F. Frozen retinal sections from at least 3 different WT eyes were co-labeled with RDS or ROM-1 (RDS-PCT1, ROM-1 mAB2H5, respectively) in green, and Syn3B (Syn3B-529) in red and DAPI in blue and imaged at 100x. Shown are single planes from a confocal stack. Arrows indicate regions of co-localization. Scale bar: 10 μm. OS: outer segment, IS: inner segment, ONL: outer nuclear layer.