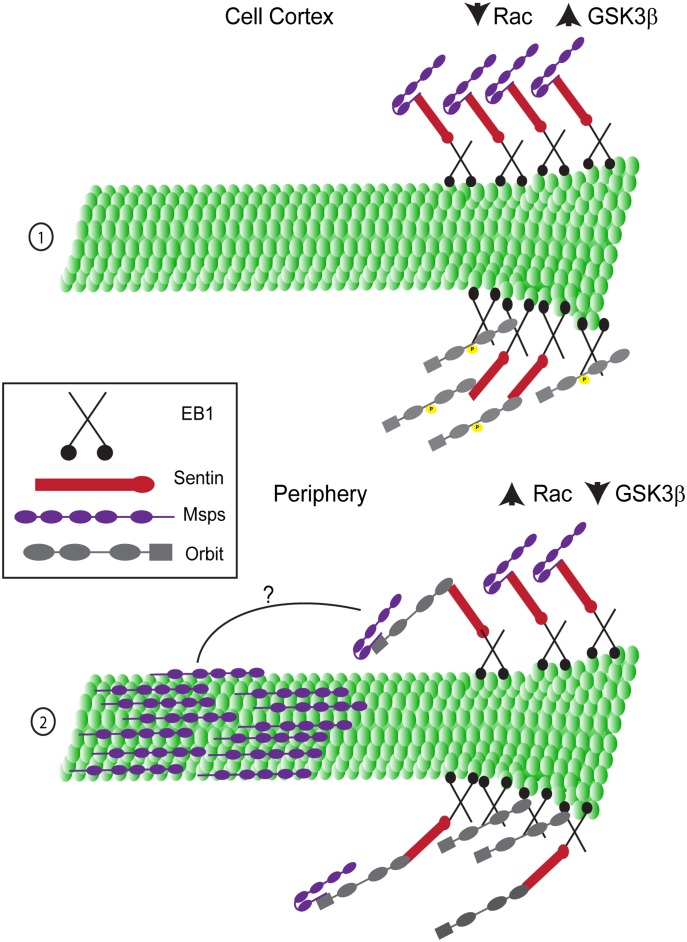
Fig 7. Model. The interaction between Msps and Orbit is required for Msps lattice association.
(1) At the plus end of a growing microtubule (green) in the cortex of the cell, Msps (purple) can localize to the plus end through its interaction with Sentin (red), which can bind EB1 (black). Msps cannot interact with the lattice and we speculate it is in a folded conformation in which its lattice binding domains are masked. Orbit (grey) is phosphorylated by GSK3β and can interact with the plus end by binding either EB1 directly or Sentin. (2) At the plus end of the microtubule in the periphery, both Msps and Orbit bind to the plus end through the same associations as in the cell cortex. Orbit is no longer phosphorylated by GSK3β and can interact with Msps. The two proteins interact through their C-termini and this allows Msps to bind to the lattice further back from the plus end, possibly by changing the conformation of Msps to expose its lattice binding domains.