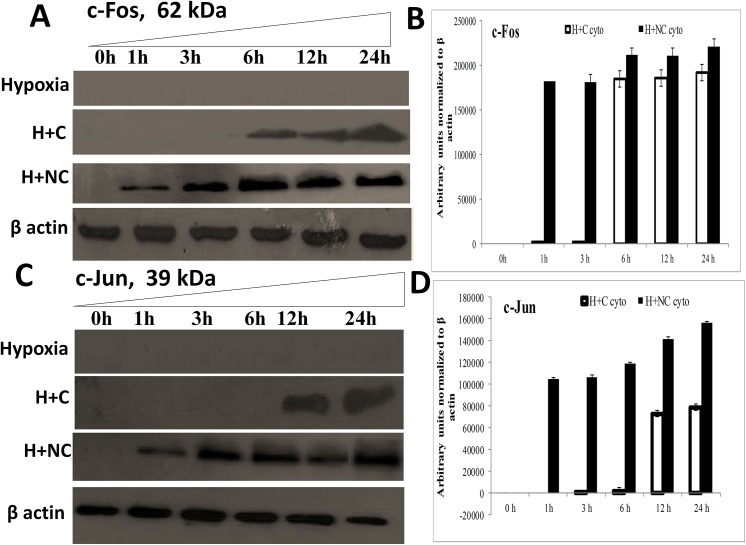
Fig 8. Nanocurcumin imparts cardio-protection in HVCM cells by activation of c-Jun/c-Fos:
Hypoxia insult prevented c-Fos and c-Jun expression in HVCM cells upto 24 h of hypoxia and thus promoted translocation of p53 to mitochondria. Treatment of HVCM cells with nanocurcumin promoted c-Fos accumulation as early as 1 h of hypoxia and prevented p53 mediated cell-death whereas curcumin treated cells showed significant up-regulation of c-Fos and c-Jun by 6–12 h of treatment under hypoxia showing that nanocurcumin is frequently available to the cells compared to curcumin. Nanocurcumin treated cells showed higher expression of negative regulators of p53 accumulation, i.e. c-Jun and c-Fos in HVCM cells under hypoxia, depicting that improved bio-availability and stability of nanocurcumin prevents hypoxia induced damage in cardiomyocytes.