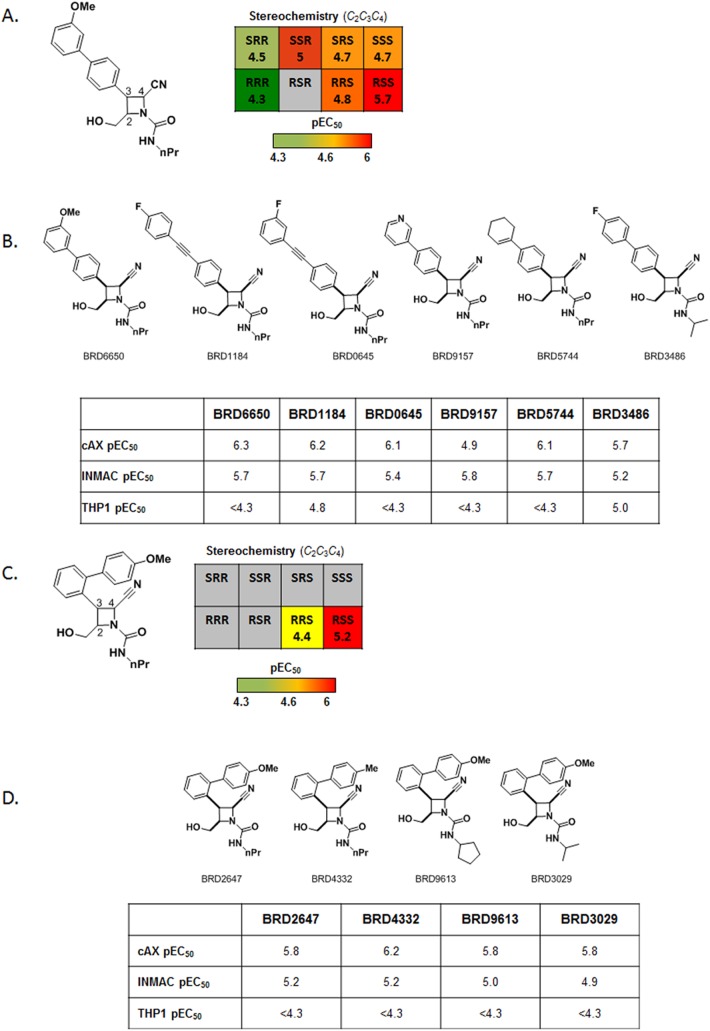
Fig 6. Compound series from the diversity-oriented synthesis library show stereochemistry-dependent selectivity as well as traditional SAR.
Compounds from two chemical scaffolds showed reproducible activity in both the novel axenic and intracellular assays. A. Analysis with the Broad's stereochemical structure activity (SSAR) viewer (see Fig E in S1 Text for an example) showed preferential activity with the RSS (C2, C3, C4) stereoisomer of Series 1 compounds. Activity of all available stereoisomers of BRD6650 indicated that the RSS isomer was the most active. B. Analogs of BRD6650 also show SAR around the original hit. Substitution on the phenyl group at the C-3 position of the azetidine ring was tolerated, as was minor variation on the urea functionality (see text for details). C. For compounds from Series 2, preferential activity was observed for the RSS stereoisomer in both thenovel axenic assay screen and the follow-up intracellular assay. D. SAR around both R1 and R2 was also observed for this series; the C-3 phenyl group could be varied with a number of ortho substituents, and variation on the urea was also tolerated.