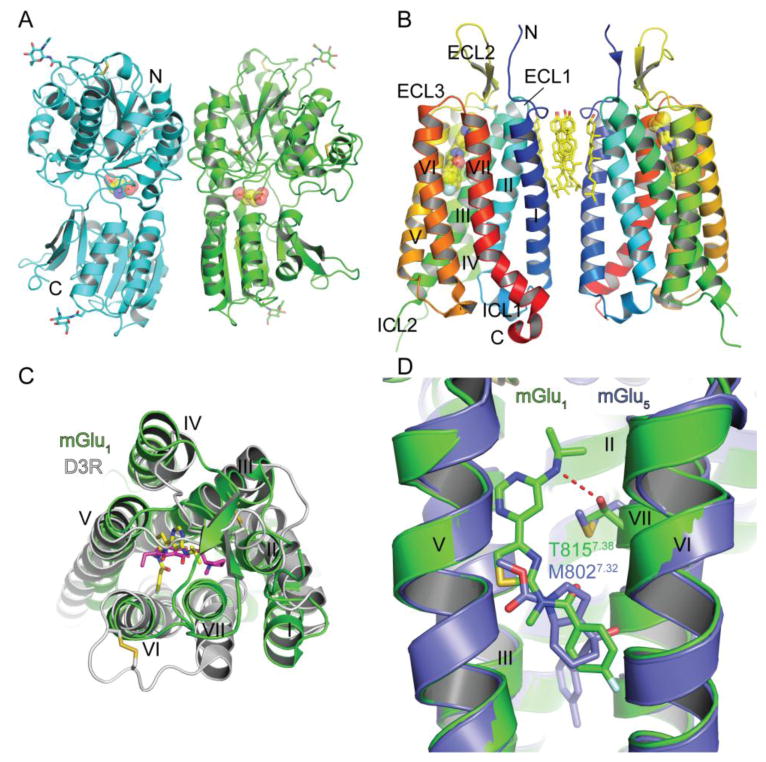
Fig. 5.
Class C GPCR structure, ligand binding sites and ligand selectivity. (A) Structure of the homodimeric extracellular venus flytrap domain of mGlu1 with a bound agonist glutamate shown in stick and space-filling representation in the orthosteric binding site (PDB: 1EWK). Glycans and disulfide bonds are shown in stick representation. (B) Structure of the mGlu1 7TM domain with a bound negative allosteric modulator FITM shown in stick and space-filling representation (PDB: 4OR2). Cholesterol molecules at the interface of the 7TM “homodimer” and disulfide bonds are shown in stick representation. (C) Superposition of the class C mGlu1 7TM domain and the class A dopamine D3 receptor with a bound antagonist eticlopride (PDB: 3PBL) viewed from the extracellular side. FITM is colored yellow and eticlopride magenta. FITM, eticlopride, and disulfide bonds are shown in stick representation. (D) Superposition of the mGlu1 and mGlu5 (PDB: 4OO9) 7TM structures highlighting a subtype selectivity determinant for negative allosteric modulator binding. FITM is colored green and mavoglurant is slate blue.