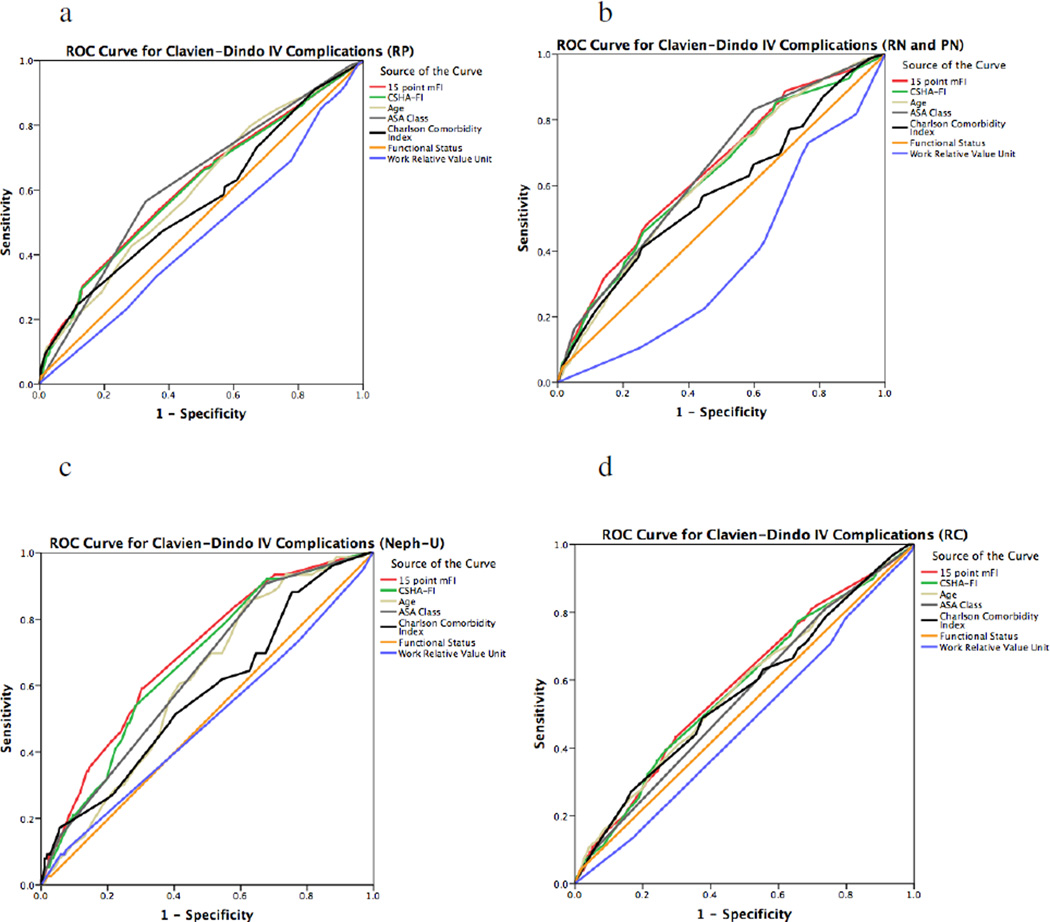
Figure 2.
Receiver operator characteristics (ROC) curve for Clavien-Dindo IV outcomes using the mFI in comparison to the existing parameters of frailty. The mFI had poor sensitivity and specificity in radical prostatectomy (RP, Fig. 1.a, C-statistic 0.615, p<0.0005), very poor sensitivity and specificity in radical cystectomy (RC, Fig. 1.d, C-statistic 0.585, p< 0.0005), poor sensitivity and specificity in nephroureterectomy (Neph-U, Fig. 1.c, C-statistic 0.691, p<0.0005), and poor sensitivity and specificity in radical and partial nephrectomy (RN and PN, Fig. 1.b, C-statistic 0.646, p<0.0005). However, the mFI equaled or surpassed the Charlson Comorbidity Index or ASA Class Risk stratification in RN, PN and Neph-U. In RP, the ASA Class outcompeted the mFI with a higher C-statistic of 0.623 in comparison to 0.615. In RC, the ASA Class also outcompeted the mFI with a higher C-statistic of 0.612 in comparison to 0.585. The 15-point mFI was superior to the 11-point CSHA-FI in all the comparisons.