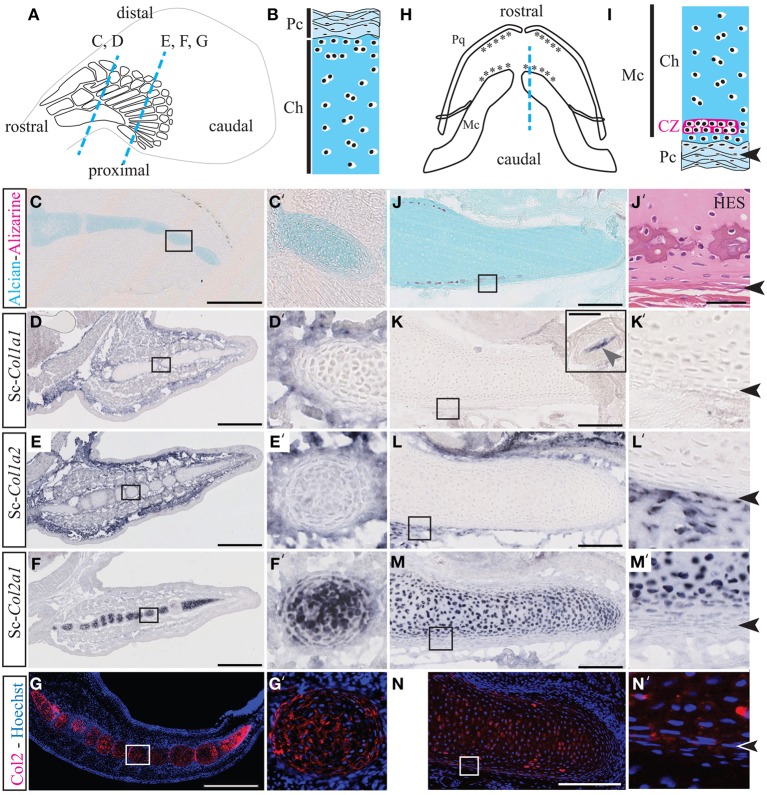
Figure 1.
Cartilage calcification and collagen expression in Scyliorhinus canicula radials and Meckel's cartilage. (A) Schematic drawing of the pectoral fin anatomy from 7 cm long S.c. embryos and of the orientation of the paraffin sections shown in C–G (blue dotted lines). Rostral and caudal refer to the embryonic axis. (B) General histology of pectoral skeletal elements, with the center of the cartilaginous element located at the bottom. (C,C') Alizarin red and Alcian blue double staining. (D–F) Gene expression patterns in the pectoral fin for Sc-Col1a1 (D), Sc-Col1a2 (E), and Sc-Col2a1 (F). (G) Immunofluorescence using an anti-Type II collagen (Col2) antibody specifically marks the pectoral fin cartilaginous condensations. (H) Schematic drawing of the jaw anatomy from 9 cm-long S.c. embryos (ventral view) and of the orientation of the paraffin sections shown in (J–N) (blue dotted line). (I) General histology of Meckel's cartilage, with the center of the cartilaginous element located at the top. The arrowheads in (I,J'–N') demarcate the fibrous perichondrium from the cartilage. (J) Alizarin red and Alcian blue double staining. (J') Higher magnification of a tesserae located in a similar region as the area boxed in (J) and stained with HES. (K–M) Gene expression patterns in the jaw for Sc-Col1a1 [the inset in (K) shows a Sc-Col1a1 positive dermal denticle from the same section], Sc-Col1a2 (L) and Sc-Col2a1 (M). (N) Immunofluorescence using an anti-Type II collagen (Col2) antibody specifically marks the cartilaginous condensations of Meckel's cartilage. Insets in (C–N) are shown at higher magnification in (C'–N'), respectively. CZ, calcification zone of the tesserae; Ch, chondroctyces; Fb, fibroblasts; Pc, perichondrium; Pq, palatoquadrate. Scale bars: (C–G), 250 μm; (J–N), 100 μm.