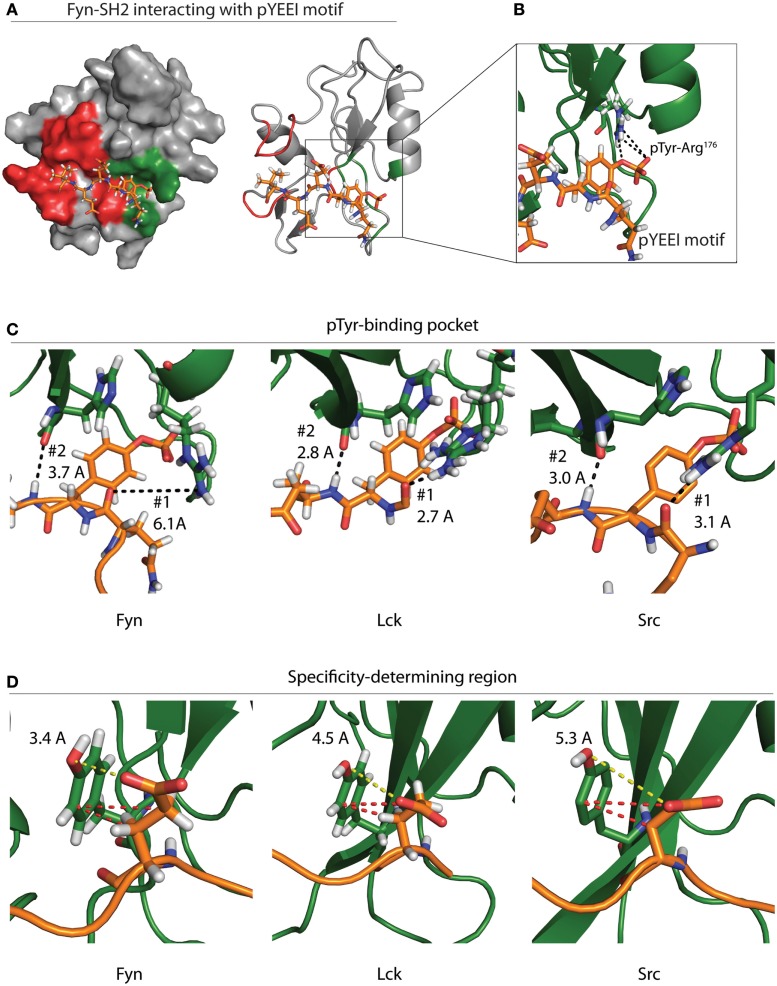
Figure 4.
Specificity of the Fyn–ADAP interaction. (A) Surface and ribbon models show the Fyn SH2 domain bound to a pYEEI peptide motif. Green shading on the surface model represents the phosphotyrosine-binding pocket, while red shading represents the specificity-determining region. The ribbon model shows that the pYEEI peptide lies orthogonal to the β-sheet of the SH2 domain. This positions the phosphorylated tyrosine in a hydrophilic pocket in between the β-sheet and the αA helix. The linear conformation of the peptide allows residues C-terminal to the phosphotyrosine to interact with other regions of the SH2 domain, which increases specificity and affinity of the Fyn–substrate interaction. Both the surface and ribbon model are derived from PDB deposition 1AOT. (B) An exploded view of the primary binding pocket highlights the interaction between the phosphotyrosine and the conserved ArgβB5 of Fyn. Salt-bridge formation at this site contributes roughly 50% of the binding energy required for the SH2 peptide interaction. (C) Comparison of different SFKs bound to pYEEI motifs show varied interactions at the phosphotyrosine-binding pocket. Ribbon models of Fyn (left), Lck (center), and Src (right) highlight bond distances between ArgαA2 of the SH2 domain and a backbone carbonyl on the target peptide (#1). Bond distances show that ArgαA2 is capable of interacting with the backbone of the pYEEI motif in Src and Lck but not in Fyn. Ribbon models also show the distance between the backbone carbonyl of HisβD4 of the SH2 domain and backbone amide of the pYEEI motif (#2). These bond distances suggest that the structure of the Fyn SH2 domain places pYEEI motifs in a more extended conformation than that seen in Src or Lck. (D) Measurements obtained from PDB depositions show the distance between TyrβD5 of the SH2 domain and the glutamate residue in the +1 position from the phosphotyrosine. The shorter distance in Fyn (left) means that hydrogen bonding is possible between TyrβD5 and the +1 glutamate residue of the pYEEI motif, while bonding is based primarily on hydrophobic interactions (red dashes) in Lck (center) and Src (right). This may provide an explanation for the ability of Fyn to act as the sole kinase responsible for recruitment of ADAP, as less hydrophobic interactions would be possible between the SH2 domain and YDGI motif of ADAP. Measurements are based on PDB depositions 1AOT for Fyn, 1LKK for Lck, and 1SPS for Src.