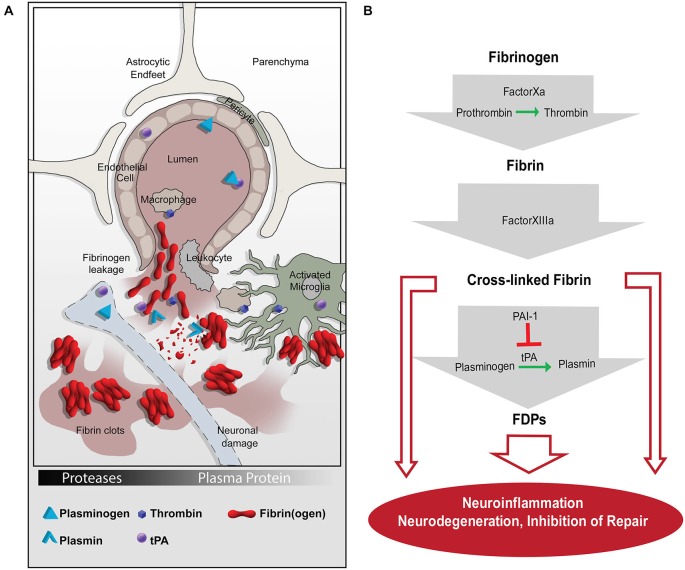
Figure 1.
The coagulation and proteolytic cascades at the neurovascular interface. (A) Fibrinogen leakage in the central nervous system (CNS) and activation of the plasminogen activation (PA) system occur following blood-brain-barrier (BBB) disruption. The molecular network of fibrin and the PA system enable inflammation and neurodegeneration via activation of microglia, macrophages, and leukocytes. (B) A series of proteolytic events converts extravasated fibrinogen into insoluble fibrin, which can be cleaved into FDPs. Fibrin and FDPs interact with cellular receptors to induce inflammation, degeneration, and repair inhibition in the nervous system. tPA, tissue plasminogen activator; PAI-1, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1; FDPs, fibrin degradation products.