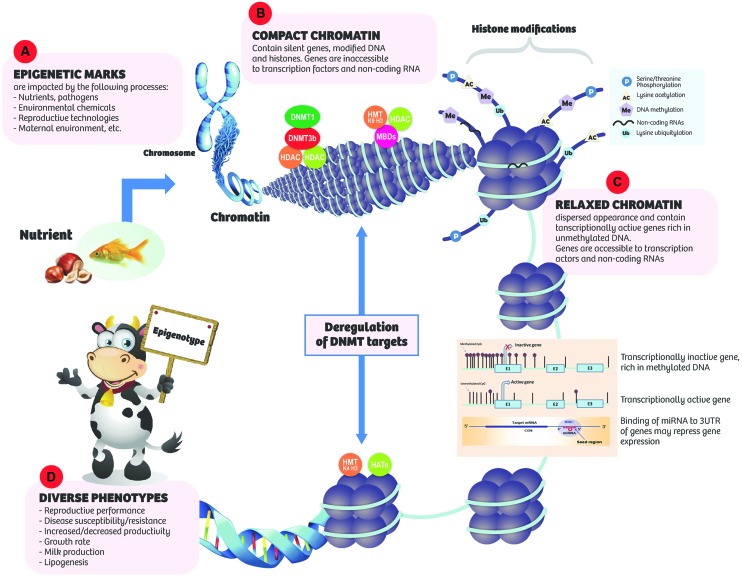
FIGURE 1.
Epigenetic marks respond to internal and environmental cues (A) resulting in various effects on chromatic conformation and gene expression. (B) Compact chromatin: tends to contain silent genes, modified DNA and histones. A number of nuclear factors such as DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs), methyl-CpG binding domain proteins (MBDs), histone methyltransferases (HMT, K9, H3), histonedeactylases (HDACs), and DNA methylation are involved in silencing gene expression. In the compact state, genes are inaccessible to transcription factors and non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs). (C) Relaxed chromatin: has dispersed appearance and is gene rich. Transcriptionally active genes are rich in unmethylated DNA. Histones are generally hyperacetylated. Histone methyltransferases (HMT, K4, H3) and acetyltransferaces (HATs) are associated with unmethylated promoters and transcriptional activity. Genes are accessible to transcription factors and ncRNAs. (D) Diverse phenotypes may result.