Figure 3.
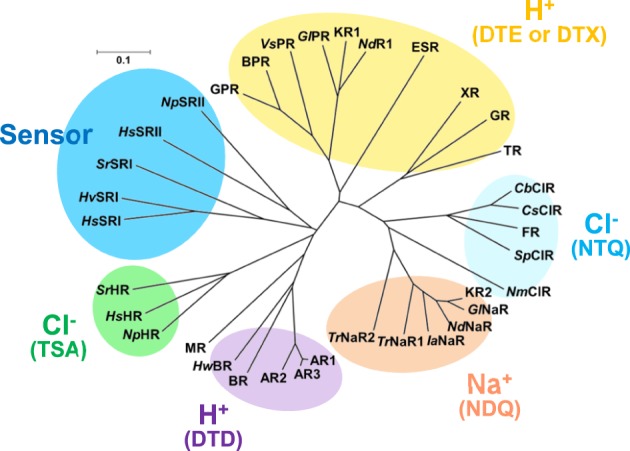
Phylogenic tree of microbial rhodopsins. This figure is modified from Inoue et al. (2015). The scale bar represents the number of substitutions per site (0.1 indicates 10 nucleotides substitutions per 100 nucleotides). Marine bacterial H+ (yellow), Na+ (orange) and Cl− (cyan) pumps have the DTE (or DTX), NDQ, and NTQ motifs, respectively, while archaeal H+ and Cl− pumps have the DTD and TSA motifs, respectively. Sensory rhodopsins from halophilic archaea and eubacteria are also shown. AR1, Archaerhodopsin-1; AR2, Archaerhodopsin-2; AR3, Archaerhodopsin-3; HwBR, BR from Haloquadratum walsbyi; MR, Middle rhodopsin; NpHR, HsHR, SrHR, HR from Natronomonas pharaonis; H. salinarum and Salinibacter ruber; HsSRI, HvSRI, SrSRI, sensory rhodopsin I from H. salinarum, Haloarcula vallismortis and S. ruber; HsSRI, NpSRI, sensory rhodopsin I from H. salinarum and N. pharaonis; VsPR, GlPR, NdR1. proteorhodopsins from Vibrio sp. AND4, Gillisia limnaea DSM 15749, Nonlabens dokdonensis DSW-6; XR, xanthorhodopsin, TR, proteorhodopsin from Thermus thermophilus; CbClR, CsClR, SpClR, NmClR, ClR from Citromicrobium bathyomarinum, Citromicrobium sp. JLT1363, Sphingopyxis baekryungensis DSM 16222 and N. marinus; GlNaR, NdNaR, IaNaR, TrNaR1, TrNaR2, NaR from G. limnaea, Nonlabens dokdonensis, Indibacter alkaliphilus, and two NaRs from Truepera radiovictrix, respectively.
