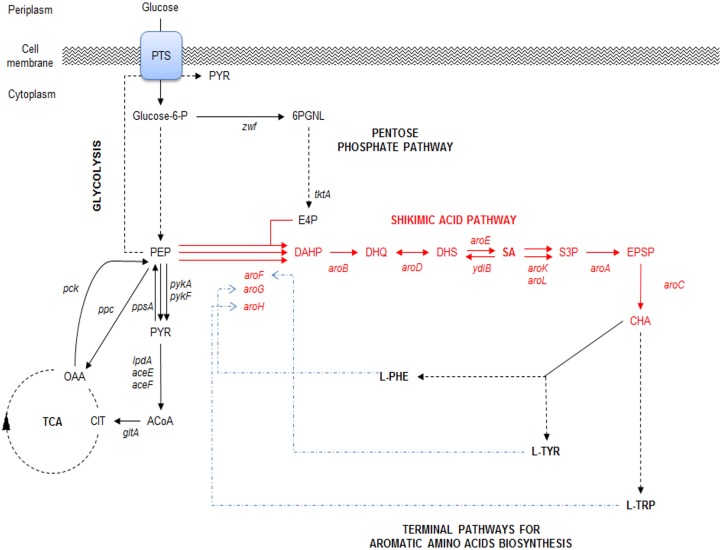
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the main glucose transport system, central carbon metabolism (CCM) (glycolysis and pentose phosphate pathways), their interconnection with SA pathway and final aromatic amino acids pathway in E. coli. PTS, phosphotransferase:PEP:glucose system. CCM key intermediates and protein encoding genes: TCA, tricarboxylic acid pathway; E4P, erythrose-4-P; PGNL, 6-phospho d-glucono-1,5-lactone; PEP, phosphoenolpyruvate; PYR, pyruvate; ACoA, acetyl-CoA; CIT, citrate; OAA, oxaloacetate; zwf, glucose 6-phosphate-1-dehydrogenase; tktA, transketolase I; pykA, pykF, pyruvate kinase II and pyruvate kinase I, respectively; lpdA, aceE, and aceF, coding for PYR dehydrogenase subunits; gltA, citrate synthase; pck, PEP carboxykinase; ppc PEP carboxylase; ppsA, PEP synthetase. SA pathway intermediates and genes: DAHP, 3-deoxy-d-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate; DHQ, 3-dehydroquinate; DHS, 3-dehydroshikimate; SA, shikimic acid; S3, SHK-3-phosphate; EPSP, 5-enolpyruvyl-shikimate 3-phosphate; CHA, chorismate; aroF, aroG, aroH, DAHP synthase AroF, AroG and AroH, respectively; aroB, DHQ synthase; aroD, DHQ dehydratase; aroE and ydiB, SHK dehydrogenase and SHK dehydrogenase/quinate dehydrogenase, respectively; aroA, 3-phosphoshikimate-1-carboxyvinyltransferase; aroC, CHA synthase. Terminal aromatic amino acids products: l-TRP, l-tryptophan; l-PHE, l-phenylalanine; l-TYR, l-tyrosine. Continuous arrows indicate single enzymatic reactions; dashed arrows show several enzymatic reactions; dashed-dotted arrows (blue) show repression of DAHPS isoenzymes allosteric regulatory circuits. Adapted from Keseler et al. (2013) and Rodriguez et al. (2014).