Figure 1.
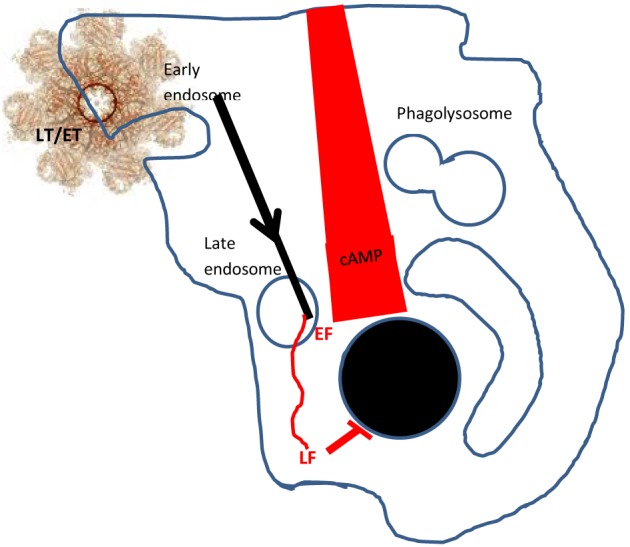
Delivery of LF and EF into the host cell. PA 83 binds to cell surface receptors and is subsequently cleaved and oligomerises to form a heptamer (PA7mer). LF and EF can bind to the PA7mer to form lethal toxin (LT) or edema toxin (ET) which associate with lipid rafts. These complexes are endocytosed (in clathrin-coated pits, facilitated by LRP6) and enter early endosomes. Subsequently, LT/ET are conveyed in vesicles to late perinuclear endosomes. The PA7mer forms a pore in the vesicle luminal wall, releasing EF to the membrane and LF to the cytosol. EF creates a gradient of cAMP emanating from the nucleus to the cell wall, whilst LF cleaves the MAP/ERK kinase (MEK) substrate to inhibit nuclear protein synthesis. Glossary: MAPKKs, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinases; ERKK, extracellular-signal-regulated kinases; MEK, MAP/ERK kinases.
