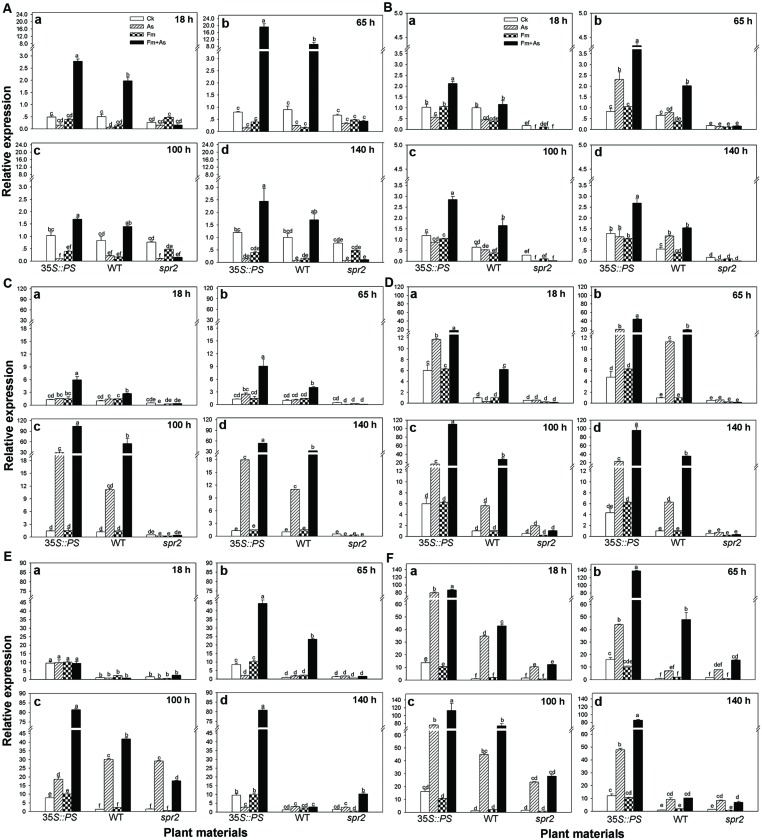
FIGURE 5.
Transcripts of defense-related genes in leaves of tomatoes with mycorrhizal colonization and pathogen infection. WT and mutant plants (35S::PS and spr2) of tomato were pre-inoculated with mycorrhizal fungus Funneliformis mosseae and later inoculated with A. solani, the causal agent of early blight disease of tomato. Quantitative real time RT-PCR was used to detect the transcripts of six defense-related genes encoding the PAL (A), LOX (B), (Pin2) (C), pathogen-related proteins (PR1) (D), β-1,3-glucanase (basic type PR-2) (E), and chitinase (PR-3) (F). Transcript levels were quantified 18 (a), 65 (b), 100 (c), and 140 h (d) after pathogen inoculation. Four treatments included: (1) CK: control plants without pathogen and mycorrhizal inoculation; (2) As: plants inoculated with A. solani only; (3) Fm: plants inoculated with F. mosseae only; (4) Fm+As: plants inoculated with both F. mosseae and A. solani. Three tomato genotypes included: (1) WT: wild type plant; (2) 35S::PS: Prosystemin-overexpressing 35S::PS plant; (3) spr2: JA biosynthesis mutant plant. Values are means ± SE from three sets of independent experiments with three pots per treatment for each set of experiments. Significant differences among treatments were tested at P = 0.05 by Tukey post hoc test.