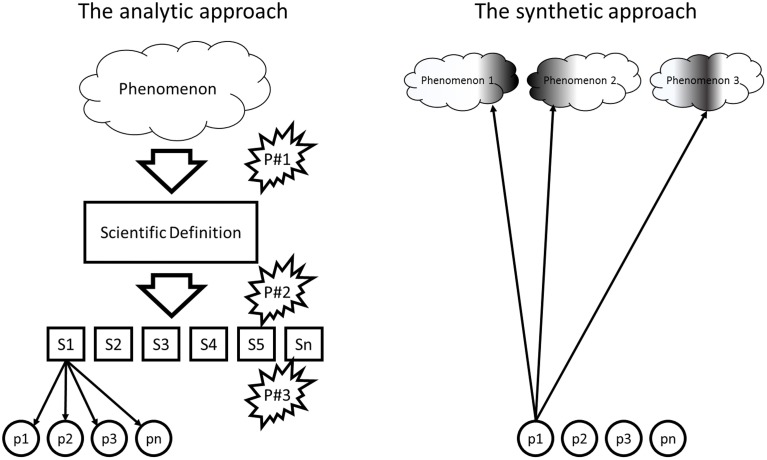
Figure 1.
The analytic and the synthetic approach to human cognition. The dominating analytic approach involves translating a real-life phenomenon into a scientific definition, which later is split into definitions of subfunctions (S1, …. Sn) and mapped onto underlying processes (p1, … pn). The flash signs refer to the three pitfalls we discuss. The alternative synthetic approach consists in investigating which aspects of different phenomena are accounted for by a particular process. Its goal is not (necessarily) to account for entire phenomena but, rather, for many aspects of many phenomena by means of the same process.