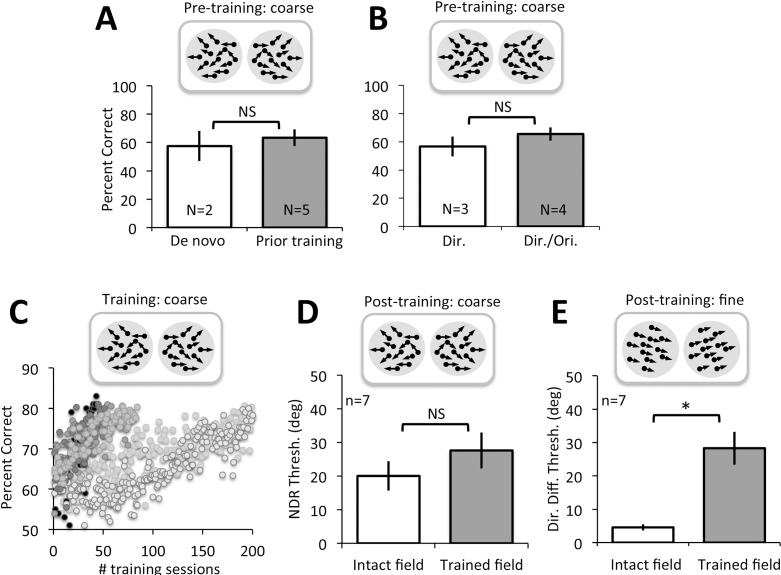
Figure 5.
Coarse and fine direction discrimination performance in CB subjects. (A) Pretraining performance for coarse, left–right global direction discrimination in subjects recruited de novo or who had undergone training as part of a previous study (Das et al., 2014). There were no significant differences between these two subject subgroups. (B) Pretraining performance for coarse, left–right global direction discrimination in subjects who received either direction discrimination training only or direction and orientation discrimination training. All subjects were equally impaired prior to the onset of training administered for the present study. (C) Example of training data for CB subjects, showing percent-correct performance on individual training sessions for the global left–right direction discrimination task. All subjects started around or just above chance, but eventually rose to ∼80% correct. (D) Following training, direction range thresholds across all subjects recovered to near-intact field levels. (E) Direction difference thresholds also improved following coarse discrimination training, but they remained significantly higher compared to direction difference thresholds measured at corresponding locations in the intact field of vision (*p = 0.003).