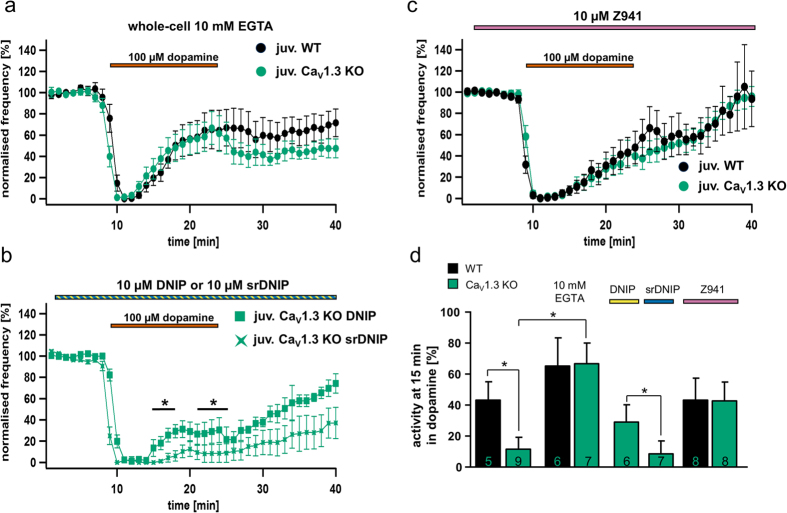
Figure 3. Calcium-dependent, sensitised D2-autoreceptor responses in SN DA neurons from juvenile Cav1.3 KO mice are mediated by T-type Ca2+ channels and the neuronal calcium sensor NCS-1.
Dopamine D2-AR experiments and SN DA data presentation are similar to that for Fig. 2. (a) Experiments in the presence of 10 mM EGTA (whole-cell current clamp), to buffer free internal Ca2+ in SN DA neurons from juvenile WT (n = 6) and Cav1.3 KO (n = 7) mice. (b) Experiments in the presence of either DNIP (yellow, D2/NCS-1 interacting peptide) or scrambled DNIP (as controls, blue, srDNIP) to block D2-AR/NCS-1 interactions in SN DA neurons from juvenile Cav1.3 KO mice (DNIP: n = 11; srDNIP: n = 10, perforated patch or on-cell recordings). Mean basal pacemaker frequencies were not affected by DNIP (see Table 1). (c) Experiments in the presence of the T-type Ca2+ channel blocker Z941 (10 μM; purple bar, perforated patch) in SN DA neurons from juvenile WT (n = 10) and Cav1.3 KO (n = 8). (d) Activity of SN DA neurons from (a–c) (and from Fig. 2a) at the last minute of dopamine application (min 15). Note that buffering of free internal Ca2+ (EGTA) is inducing prominent D2-AR desensitisation in both SN DA neurons from juvenile WT and KO mice, while DNIP (but not srDNIP), as well as Z941, both introduce WT-like D2-AR desensitisation in SN DA neurons from juvenile Cav1.3 KO mice. All data are shown as mean ± SEM, WT data in black and KO data in green. Significant differences are marked by asterisks. Data values and statistics are detailed in Table 1.