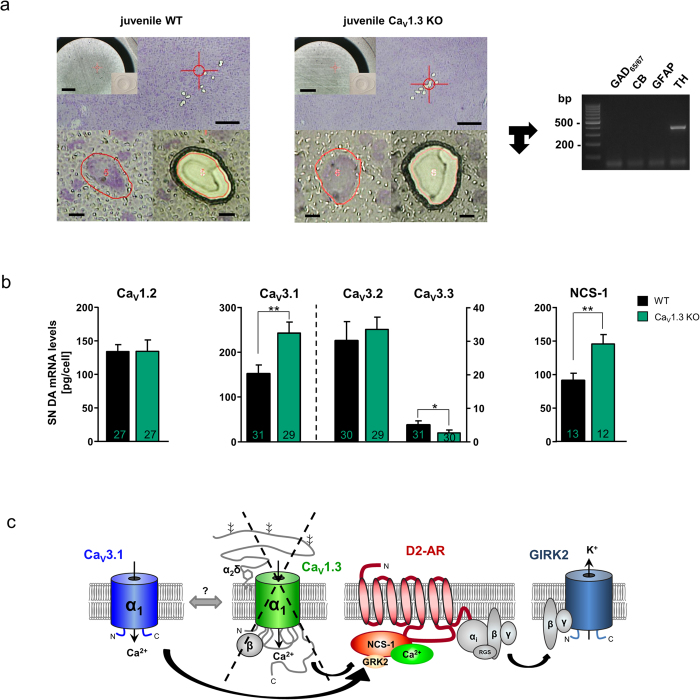
Figure 6. Compensatory up-regulation of Cav3.1 T-type Ca2+ channel subunits and of NCS-1 mRNA in SN DA neurons from juvenile Cav1.3 KO mice.
(a) Overview of WT (left) and Cav1.3 KO mouse (middle) coronal midbrain sections after UV-laser-microdissection (UV-LMD) of 10 individual SN DA neurons each. Scale bars: 250 μm. Inserts: photograph of the reaction-tube-cap for inspection of collection of all 10 neurons after UV-LMD, prior to cell lysis and reverse transcription. Scale bars: 500 μm. Lower left/middle: individual SN DA neurons before and after UV-LMD. Scale bars: 10 μm. Right: Multiplex nested PCR results (2% agarose-gel-electrophoresis). All analysed SN DA cDNA pools were PCR-positive for tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) and negative for calbindind28k (CB), for GABAergic markers (GAD65/67) and for astroglial marker (GFAP). (b) Cell-specific quantitative RT-PCR data of the L-type Ca2+ channel subunit Cav1.2, of the T-type Ca2+ channel subunits Cav3.1, Cav3.2, and Cav3.3, and of the neuronal calcium sensor NCS-1, for SN DA neurons from juvenile WT and Cav1.3 KO mice (n numbers given in bars). Data given as [pg/cell] in respect to a cDNA standard curve, generated from WT mouse midbrain tissue. All data given as the mean ± SEM. WT data given in black, KO data in green. Note significantly higher mRNA-levels of Cav3.1 and NCS-1 in SN DA from Cav1.3 KO. (c) Cartoon summarising the postulated molecular mechanism of altered dopamine NCS-1/D2-AR/GIRK2 channel signalling in SN DA neurons from juvenile Cav1.3 KO mice: Chronic loss of Cav1.3 L-type-Ca2+ -channels (with its regulatory β- and α2δ subunits) that sensitises D2-ARs in response to extracellular dopamine via the neuronal calcium sensor NCS-1 is functionally compensated in SN DA neurons by Cav3.1 T-type-Ca2+ -channels, boosting calcium-dependent D2-AR/NCS-1 interaction, that prevent GRK2-mediated D2-AR phosphorylation and thus β-arrestin-mediated receptor internalisation and desensitisation—resulting in enhanced GIRK2- mediated SN DA pacemaker-activity inhibition. Abbreviations: D2-AR: D2-autoreceptor, GIRK2: G-protein-coupled, inwardly rectifying K+ channel 2, GRK2: G-protein coupled kinase 2, RGS: regulator of G-protein signalling; for details see text.