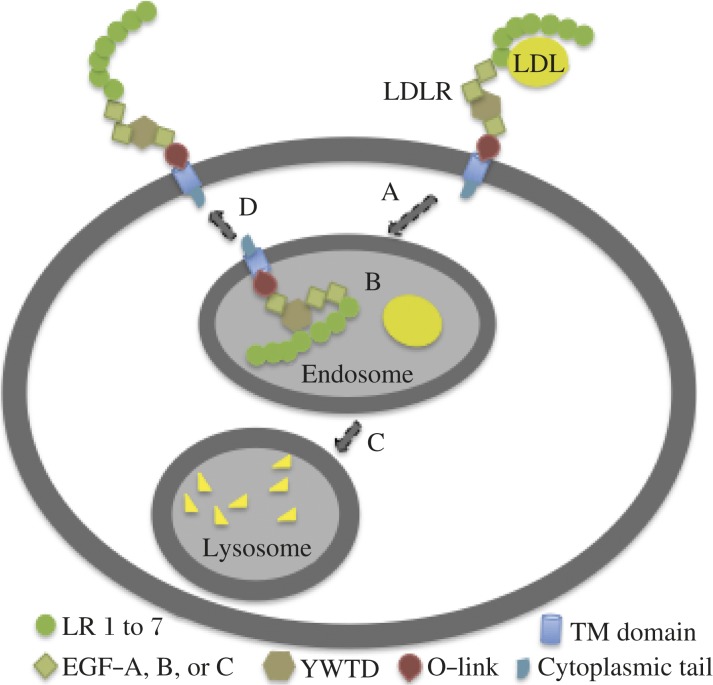
Fig. 1. LDLR-mediated LDL uptake.
A: LDL binds to the LDLR on the cell surface, enters into cells via clathrin-dependent endocytosis, and delivered to endosomes[62]. B: The conformation of the LDLR is changed to a close conformation in the low pH environment of the endosome, which promotes the release of the bound LDL[10]. C: Released LDL is delivered to lysosomes for degradation. D: The LDLR is recycled to the cell surface.