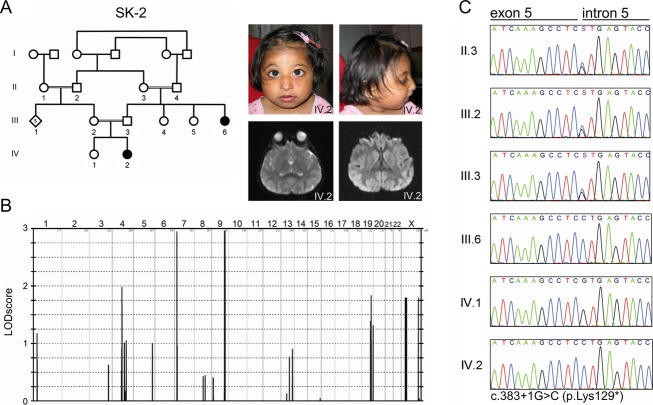
Figure 2.
Clinical and molecular findings in family SK-2 with Seckel syndrome. (A) Pedigree of the consanguineous family from Pakistan, front and lateral photographs and MRI images of the affected individual IV.2 at the age of 3 years. (B) Parametric linkage analysis of family SK-2. LOD scores were calculated with ALLEGRO, and the highest scores were obtained for markers on chromosomes 7 and 9. (C) Electropherograms of the identified homozygous CDK5RAP2 mutation (III.6 and IV.2) compared with heterozygous carrier (II.3, III.2, and III.3) and wild-type sequences (IV.1).