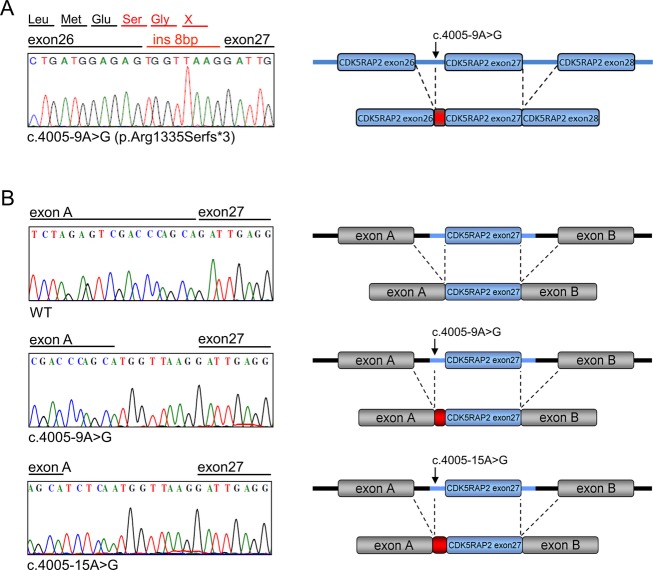
Figure 3.
Transcriptional consequences of identified c.4005-9A>G mutation in CDK5RAP2. (A) Left: Electropherogram of cDNA derived from the CDK5RAP2 transcript from patient II.1 of family SK-1 carrying the homozygous CDK5RAP2 c.4005-9A>G mutation shows alternative splicing of exon 27 leading to an 8 bp insertion and thereby to a frame-shift and a premature stop codon. Right: Schematic representation of the alternatively spliced transcript. (B) Results from the exon-trapping assay. Left: Electropherograms of cDNA-PCR products generated from the wild-type and mutant constructs: The c.4005-9A>G mutation leads to a complete loss of the original splice-site and to insertion of 8 bp. The previously described c.4005-15A>G mutation has a similar effect leading to insertion of 14 bp. Right: Schematic representation of the constructs used for the assay and of the observed alternatively spliced transcripts. Exon A and exon B represent artificial exons of the pSPL3 splicing vector.