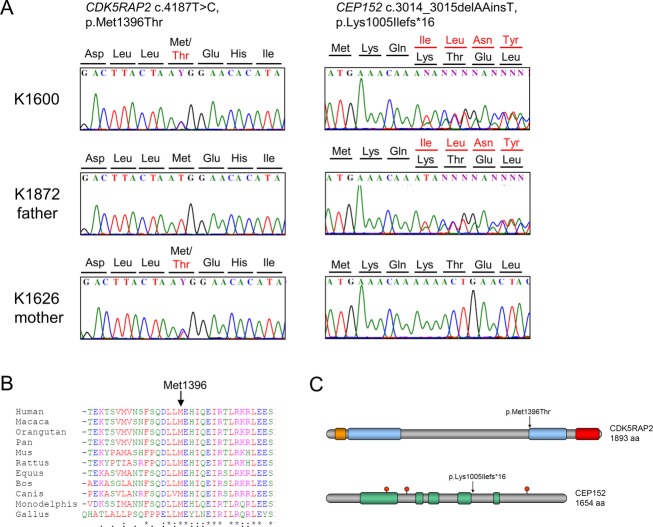
Figure 5.
Molecular findings in patient K1600 with Seckel syndrome. (A) Left: Electropherogram of identified heterozygous CDK5RAP2 mutation compared with heterozygous carrier sequence of the mother (K1626) and wild-type sequence of the father (K1872). Right: Electropherogram of identified heterozygous CEP152 mutation compared with heterozygous carrier sequence of the father (K1872) and wild-type sequence of the mother (K1626). (B) Amino acid sequence alignment of CDK5RAP2 proteins of different species shows the highly conserved methionine at position 1396. (C) Schematic view of CDK5RAP2 and CEP152 protein domains. Upper picture: Protein structure of CDK5RAP2 with structural maintenance-of-chromosomes (SMC) domains (blue), γ-tubulin ring complex-binding domain (orange), and pericentrin interaction domain (red). Lower picture: Protein structure of CEP152 with predicted coiled-coil domains (green) and Thr/Ser-phosphorylation sites (red). The positions of the mutations are marked by arrows.