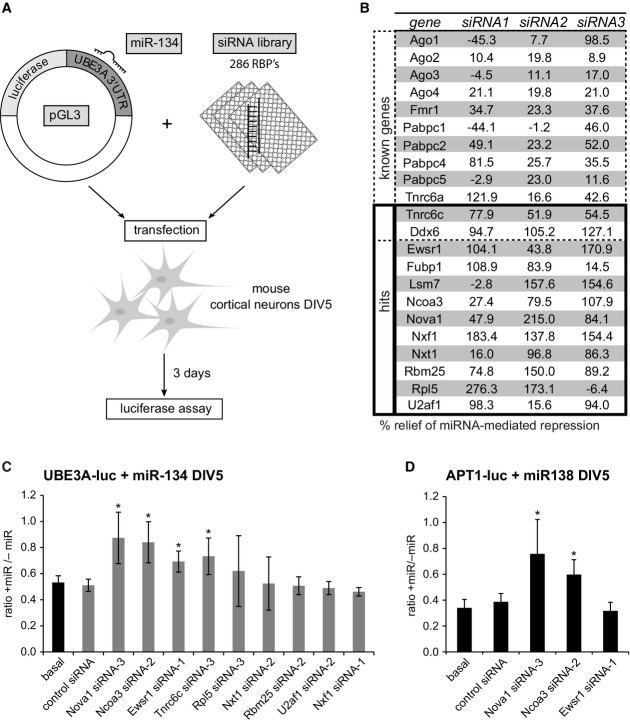
Figure 1.
Identification of 12 RNA-binding proteins required for miR-134 repressive function in primary neurons using siRNA-based screening
- Setup of the RNAi screen in mouse primary cortical neurons. Neurons (5 days in vitro (DIV)) were co-transfected with the miR-134-responsive pGL3-UBE3A-3′UTR luciferase reporter (pGL3-UBE3A-luc) together with miR-134 duplex RNA and siRNA (one per condition) directed against 286 RBPs expressed in the mouse cortex (3 siRNAs per RBP). Luciferase activity was determined 3 days after transfection.
- Table of genes which are either known to be involved in the regulation of miRNA activity (“known genes”) or whose knockdown led to an at least 50% relief of miRNA-mediated repression for at least two out of the three siRNAs tested (“hits”). Values are the average of three replicate experiments and represent the percent relief of miRNA-mediated repression for the indicated siRNA compared to a condition without siRNA. Note that two known genes (Tnrc6c, Ddx6) were also present within the 12 hits.
- Luciferase reporter assay in primary rat cortical neurons transfected with pGL4-UBE3A-luc and the indicated siRNAs in the presence or absence of miR-134 duplex RNA. The ratio of normalized luciferase activity from neurons with (“+miR”) to neurons without co-transfected miR-134 (“−miR”) is plotted. Values are the average from three independent experiments ± standard deviation. *P < 0.05 (unpaired t-test compared to control siRNA).
- Luciferase reporter assay as in (C) with pGL4-APT1 3′UTR (APT1-luc) in the presence (“+miR”) or absence (“−miR”) of miR-138. n = 3. *P < 0.05 (unpaired t-test compared to control siRNA).