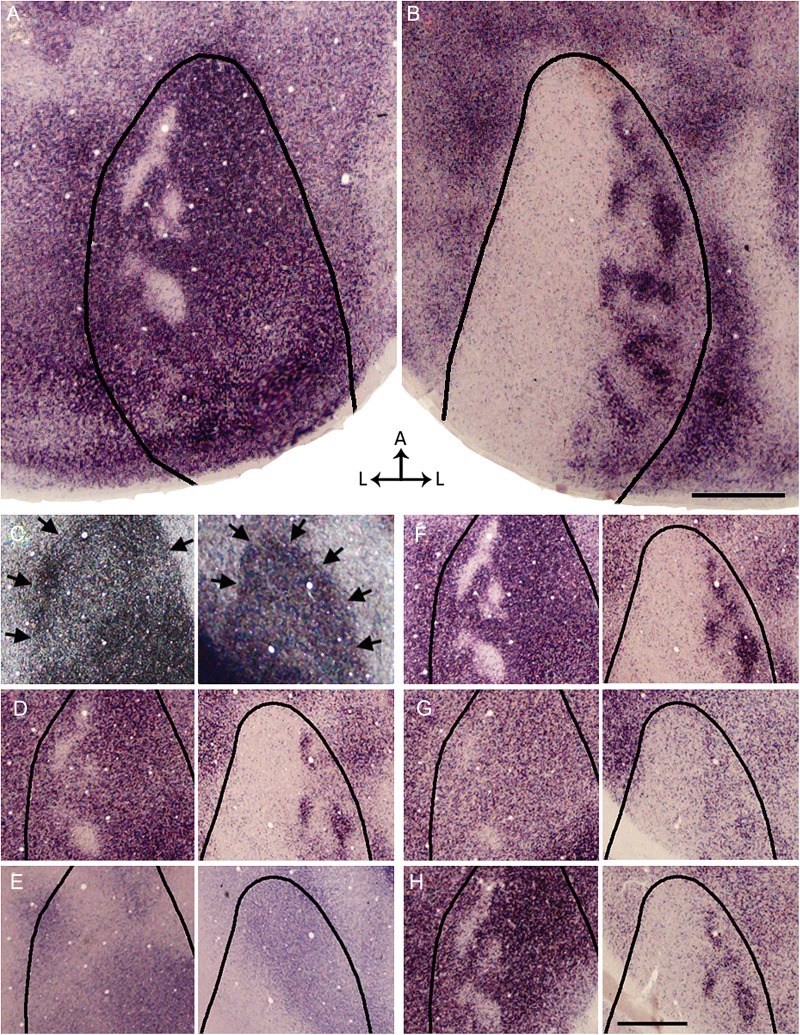
Figure 7.
Functional segregation of contralateral and ipsilateral eye domains in V1 demonstrated with ISH for Zif268 after an injection of TTX into the left eye, leaving only the right eye active. (A,B) Overall patterns of Zif268 expression in the left (A) and right (B) hemispheres reconstructed from 3 and 4 tangential sections, respectively. Areas of strong Zif268 expression, corresponding to activity driven by the right eye, appear darkly stained. In the left V1 (A), pale patches presumably correspond to domains innervated by the silent left eye. In the right V1 (B), dark patches presumably correspond to domains driven by the active right eye. The black outlines indicate the border of V1 as revealed in the myelin pattern. (C–H) Left and right images in each pair are from the left and right hemispheres, respectively. (C) Pattern of myelination used to determine the border of V1 (arrows). The complete myelination patterns for V1 were available for delineating the border of V1 in A,B. (D) Pattern of Zif268 expression in supragranular layers. (E) Pattern of ROR β labeling in section through Layer 4 (Hirokawa et al. 2008). (F) Pattern of Zif268 expression is strongest at the level of Layer 4, immediately below the section stained for ROR β (E). (G) The pattern of Zif268 expression weakens and becomes less discernible at approximately the level of Layer 5, but it becomes stronger in sections through Layer 6 (H). Scale bars = 1.0 mm.