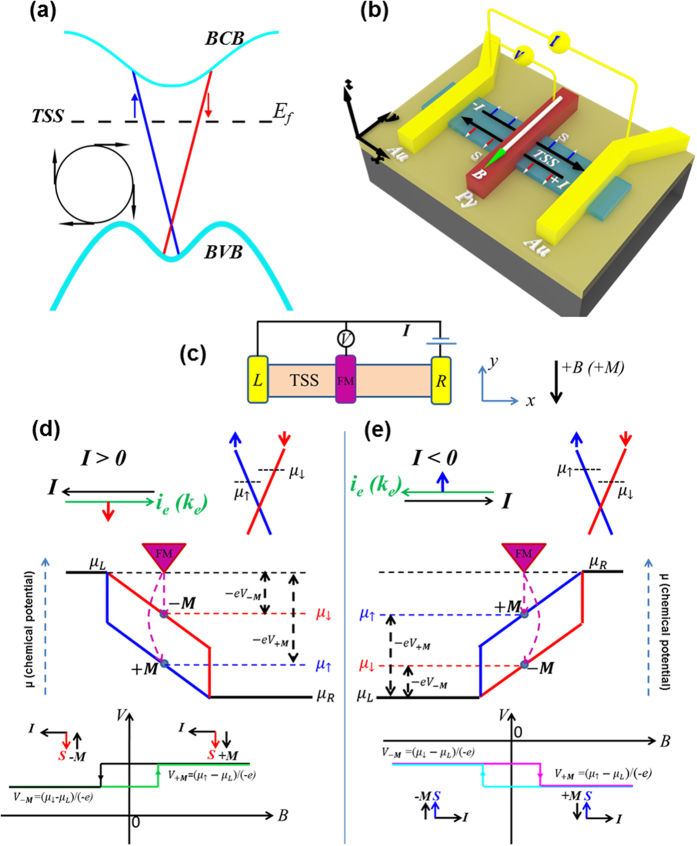
Figure 1. Schematic of topological surface state and spin potentiometric measurement.
(a) Schematic band structure around the Γ point of a topological insulator (TI) near the top surface, showing TSS, bulk valence band (BVB) and bulk conduction band (BCB). Dashed line indicates the Fermi level, Ef, and arrows indicate the (in-plane) spin polarization directions of TSS. Inset shows the schematic TSS Fermi surface with its characteristic “left-handed” spin helicity. (b) Schematic 3D device structure used in the potentiometric measurement showing the three-terminal electrical connections as well as the current-induced spin-polarization of the TSS on the top surface. The TI surface defines the x-y plane and the surface normal the z direction. The two outside nonmagnetic (eg., Au) contacts are used to inject bias currents, and the middle ferromagnetic (eg., Py) contact is magnetized by an in-plane magnetic field B (labeled) along its easy axis (y-direction). The middle ferromagnetic contact is a tunneling probe that draws no current. (c–e) Theoretical understanding of the spin potentiometric measurement in the linear response regime probing the current-induced spin polarization due to TSS on the top surface of a 3D TI for both (d) positive and (e) negative bias currents, based on the spin-dependent electrochemical potentials.