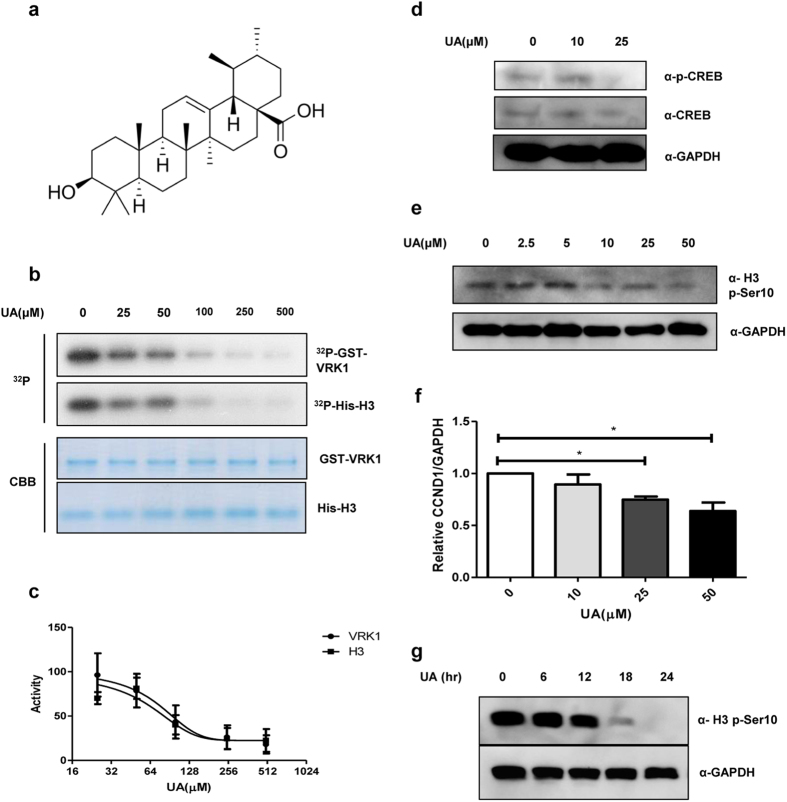
Figure 1. Inhibitory effect of UA on VRK1 kinase activity.
(a) Chemical structure of UA. (b) in vitro kinase assay with His-H3 and GST-VRK1 was performed with increasing concentrations of UA (0.0, 25, 50, 100, 250, or 500 μM); GST-VRK1 and His-H3 were then stained with Coomassie blue. (c) Quantification of VRK1 auto-phosphorylation and histone H3 phosphorylation shown in panel (b). Data represent the mean of three independent experiments ± standard error of means (SEMs). (d) Immunoblotting of A549 cell lysates treated with the indicated concentration (0.0, 10, or 25 μM) of UA. (e) Immunoblotting of lysates from A549 cells treated with the indicated concentration (0.0, 2.5, 5.0, 10, 25, or 50 μM) of UA. (f) Alteration in relative CCND1 mRNA levels after treatment with the indicated concentrations of UA was determined by quantitative real-time PCR; CCND1 mRNA levels were normalized to GAPDH mRNA; error bars indicate the SEM, and asterisk (*) represents P-value < 0.05. (g) Immunoblotting of A549 cell lysates treated with UA for the indicated times (0, 6, 12, 18, or 24 hr).Immunoblotting was performed using the indicated antibodies, and GAPDH was used as the loading control in all experiments.