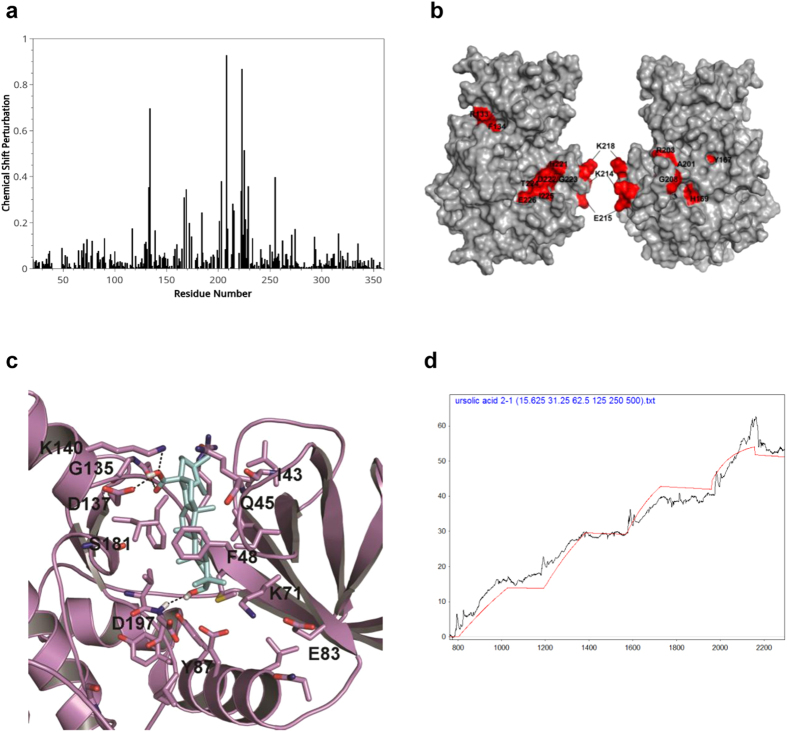
Figure 2. NMR titration assay and in silico modeling for interaction of UA with VRK1.
(a) NMR titration experiments with VRK1 and UA. Spectrum of chemical shift perturbations versus amino acid residues of the VRK1 protein after binding of UA. (b) Mapping of chemical shift perturbations on the VRK1 protein. Most of the perturbed residues (shown in red) are located close to the catalytic domain of VRK1. (c) Binding pose of UA into active site of VRK1 kinase domain. The carboxyl moiety on UA interacts with main chain carbonyl atoms of G135, side chain atoms of D137 and K140 residues via hydrogen bondings. Likewise the 3-hydroxyl moiety is also engaged in hydrogen bonding interaction with D179 main chain amide atoms. The steroid nucleus makes strong hydrophobic interactions with F48, F134, L184, V69, I51 and K71 residues that outline the VRK1 kinase domain (d), SPR detection for the interaction of UA with VRK1. The data were obtained by kinetic titration method with sequential injection of analytes without regeneration steps.