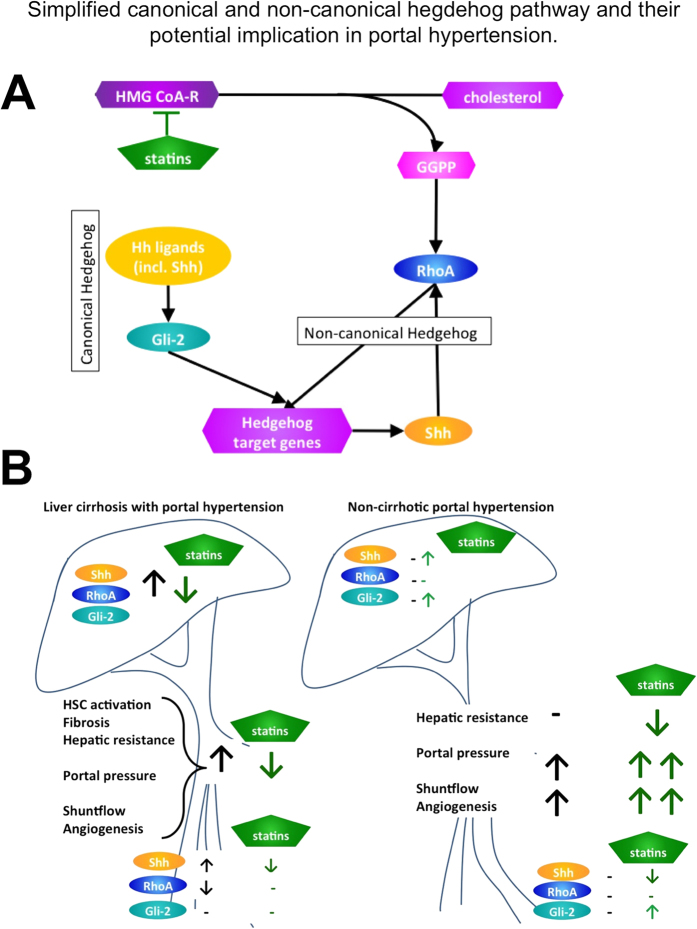
Figure 1. Simplified canonical and non-canonical hegdehog pathway and their potential implication in portal hypertension.
(A) Statin inhibit RhoA activation by hindering its isoprenylation by depletion of geranylgeranyl-pyrophosphate (GGPP). RhoA seems also to play a role in the non-canonical Hedgehog-signaling (Hh). This crosstalk between RhoA/Rho-kinase and Hh-pathway might be mediated by Shh and is Gli-independent. The canonical Hh-pathway is activated by Hh ligands, which after several steps activates Gli. Gli enhances transcription of downstream target genes. (B) Statins decrease fibrosis and lower portal hypertension in animals and humans with liver cirrhosis by blunting the RhoA/Rho-kinase-pathway and downregulation of canonical and non-canonical Hh-pathway in myofibroblastic HSCs. The non-canonical Shh/RhoA-signaling seems to play a major role in the extrahepatic angiogenesis in cirrhosis, whereas Gli-2 is a predominant mediator of canonical Hh-pathway in non-cirrhotic portal hypertension potentially mediating angiogenesis and aggravation of portal hypertension.