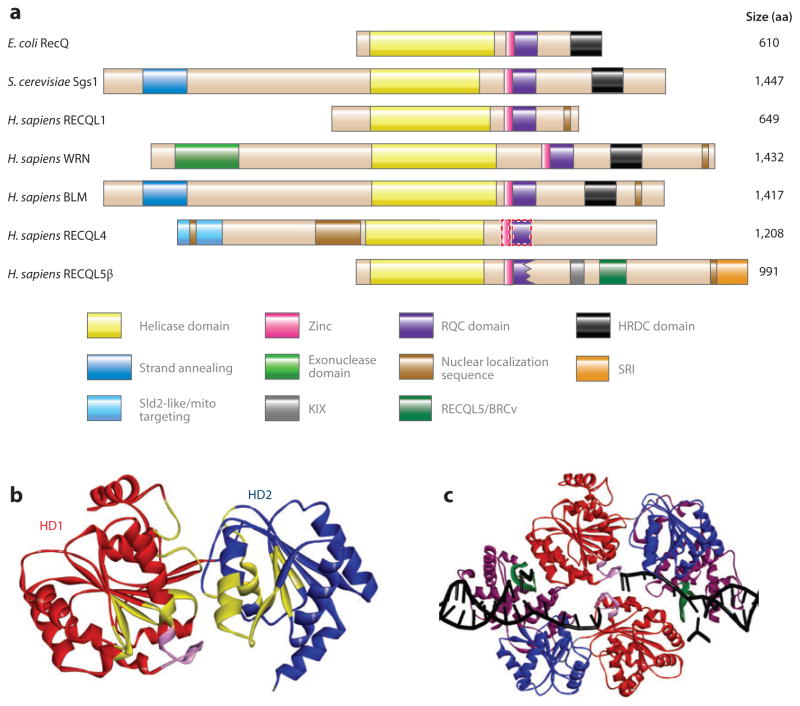
Figure 1.
RecQ helicase protein family. (a) The domain structure of RecQ helicases from Escherichia coli, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and Homo sapiens. Homologous domains are represented with solid-color boxes outlined with solid lines; the tentatively assigned zinc and RQC domains of RECQL4 are represented by rectangles outlined with dotted lines. (b) The helicase domains of human RECQL1, based on Protein Data Bank (PDB) identifier 2WWY (24). The structure includes two RecA-like domains, helicase domains 1 [HD1 (red )] and 2 [HD2 (blue)], and an ATP-binding cleft. The conserved helicase motifs are in yellow, and the aromatic loop is in pink. (c) The truncated RECQL1 bound to DNA is based on PDB 2WWY. The RQC domain is in purple, the β-hairpin is in green, and the DNA is in black. Abbreviation: aa, amino acid.