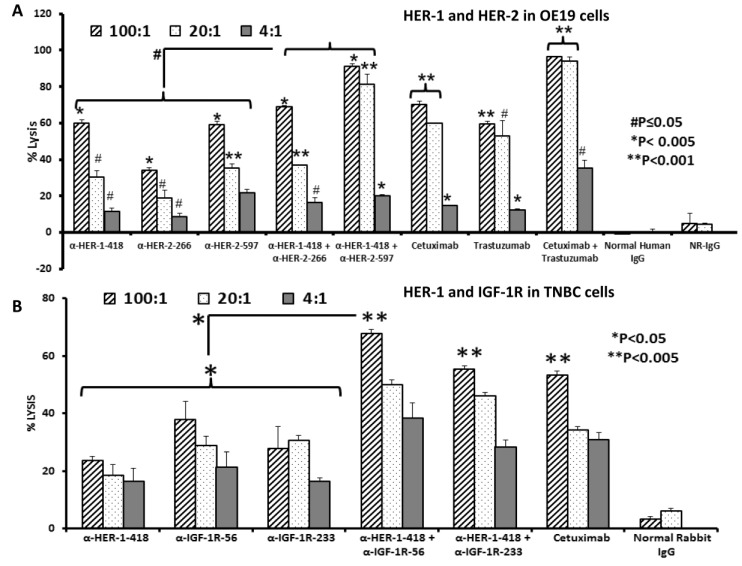
Figure 2.
Co-targeting HER-2 and HER-1 or IGF-1R and HER-1 causes greater induction of ADCC in EC and TNBC. OE19 or MDA-MB-231 cells were used as target cells and were seeded and incubated in the presence of human PBMCs at different effector: Target cell ratios (100:1, 20:1, 4:1). Cells were then treated for one hour with peptide vaccine antibodies prior to cell lysis. The aCella-tox kit (Cell Technology, Inc.; Fremont, CA, USA) was used to measure the relative amount of ADCC; cell lysis was measured according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Results represent an average of two different experiments performed in triplicate and display the % lysis of treatment groups when compared to 100% target cell lysis. Normal human and rabbit IgG (Pierce, Rockford, IL, USA) were used as a negative control; cetuximab and trastuzumab were positive controls. In EC cells, at a 100:1 ratio (A), single treatment with the anti-HER-2 and anti-HER-1 peptide vaccine antibodies showed significant induction of ADCC (* p < 0.005), but combination treatment using the anti-HER-1-418 and anti-HER-2-597 or anti-HER-1-418 and anti-HER-2-266 peptide vaccine antibodies caused greater induction of ADCC (# p < 0.05) than single treatment alone. In TNBC cells, at a ratio of 100:1 (B), anti-HER-1-418, anti-IGF-1R-56, and anti-IGF-1R-233 peptide vaccine antibodies induced significant levels of ADCC as compared to negative control (* p < 0.05). The combination of anti-HER-1-418 and anti-IGF-1R-56 induced significantly higher levels of ADCC compared to single treatment alone (* p < 0.05).